Publications
Activin A
Huang, T et al.
Inhibition of PRC2 enables self-renewal of blastoid-competent naive pluripotent stem cells from chimpanzee
Zorzan I, Pellegrini M, Arboit M et al.
The transcriptional regulator ZNF398 mediates pluripotency and epithelial character downstream of TGF-beta in human PSCs
Beucher A, Miguel-Escalada I, Balboa D et al.
The HASTER lncRNA promoter is a cis-acting transcriptional stabilizer of HNF1A
Bao M, Cornwall-Scoones J, Sanchez-Vasquez E et al.
Stem cell-derived synthetic embryos self-assemble by exploiting cadherin codes and cortical tension
Meek S, Watson T, Eory L et al.
Stem cell-derived porcine macrophages as a new platform for studying host-pathogen interactions
Azami T, Theeuwes B, Ton M-LN et al.
STAT3 signalling enhances tissue expansion during postimplantation mouse development
Balmas E, Ratto ML, Snijders KE et al.
Single Cell Transcriptional Perturbome in Pluripotent Stem Cell Models
Guo M, Wu J, Chen C et al.
Self-renewing human naïve pluripotent stem cells dedifferentiate in 3D culture and form blastoids spontaneously
From the lab of José Silva, Guangzhou Laboratory
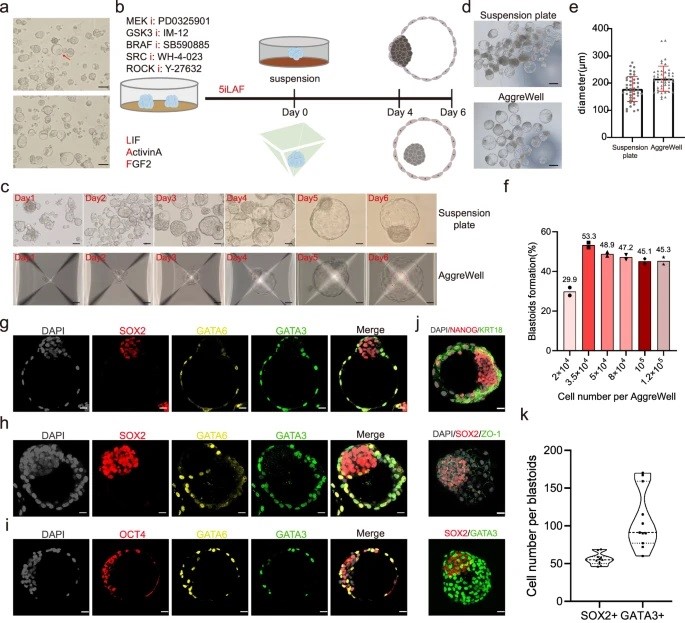
A huge challenge in understanding human early embryo cell fate is due to limited access and ethical concerns. Recent research, however, from José C. R. Silva’s lab at Guangzhou National Laboratory, drawing from single-cell sequencing, suggests a conserved lineage specification process between human and mouse embryos. Blastoids, emerging models for early embryo development, generated solely from hnPSCs, offer insights into blastocyst formation without altering culture conditions. Self-renewing human naïve pluripotent stem cells (hnPSCs) spontaneously form blastoids in 3D culture, mimicking early human blastocysts. This process, mediated by the GSK3 inhibitor IM-12 in 5iLAF medium, involves upregulation of oxidative phosphorylation genes. hnPSCs dedifferentiate into E5 embryo-like intermediates, expressing SOX2/OCT4 and GATA6, which specify trophoblast fate by day 3, coinciding with blastoid formation. This was a fantastic paper to read as it is clear how this spontaneous blastoid formation highlights the importance of culture conditions and provides a new platform to study human embryo development in vitro, potentially reshaping our understanding of hnPSCs and embryo development.
Farbergshagen, AC
Role of mechanotransduction in pancreatic endocrine cell fate acquisition in SC-islets
DOI: Thesis
Blackford SJI, Yu TTL, Norman MDA et al.
Validation of Current Good Manufacturing Practice Compliant Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Hepatocytes for Cell-Based Therapy
Truszkowski L, Bottini S, Bianchi S et al.
Refined home-brew media for cost-effective, weekend-free hiPSC culture and genetic engineering
Used:
- Recombinant human activin A protein (Qk001)
- Recombinant human FGF-2 (145 aa) protein (Qk025)
- Recombinant human FGF-2 (154 aa) protein (Qk027)
- Recombinant human BMP-4 protein (Qk038)
- Recombinant human NRG-1 protein (Qk045)
- Recombinant FGF2-G3 (145 aa) protein (Qk052)
- Recombinant FGF2-G3 (154 aa) protein (Qk053)
- Recombinant human TGF-β3 protein (Qk054)
- Recombinant human TGF-β1 PLUS™ protein (Qk010)
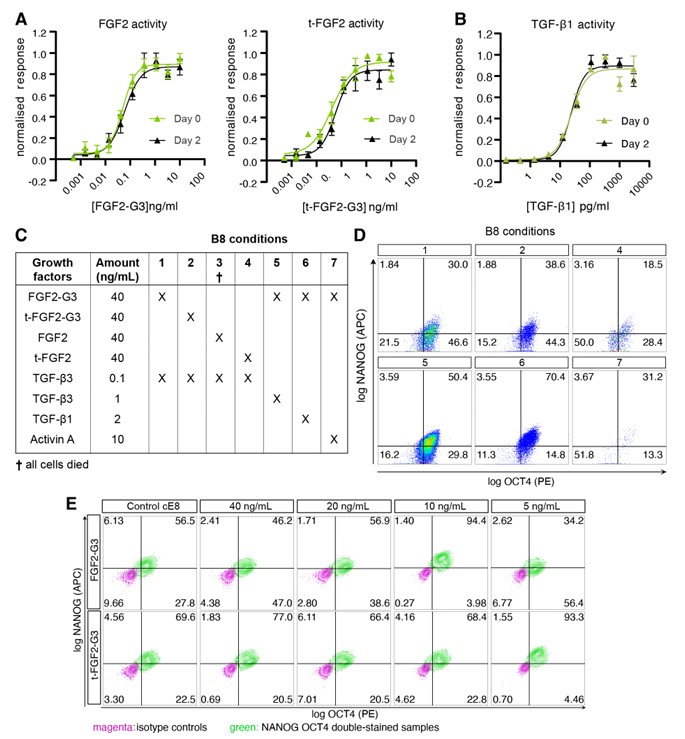
Cell therapy is becoming a possibility for many previously untreatable conditions, and it should be accessible to everyone. Creating a cost-effective, reliable and reproducible way of culturing human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) in a range of research labs, and allowing large scale culture for gene-editing purposes takes us one step closer to this.
Using high potency thermostable Qkine 145 amino acid FGF-G3 reduce FGF-2 use 8-fold and for weekend-free culture reduced media use by 57%. This makes hiPSCs a more accessible model for many labs doing basic and translational research.
Militi S, Nibhani R, Jalali M and Pauklin S.
RBL2-E2F-GCN5 guide cell fate decisions during tissue specification by regulating cell-cycle-dependent fluctuations of non-cell-autonomous signaling
Rosa VS, Sato N and Shahbazi MN et al.
Protocol for generating a 3D culture of epiblast stem cells
Drozd AM, Mariani L, Guo X, Goitea V, Menezes NA and Ferretti E.
Progesterone Receptor Modulates Extraembryonic Mesoderm and Cardiac progenitor Specification during Mouse Gastrulation
Weatherbee BAT, Gantner CW, Iwamoto-Stohl LK et al.
Pluripotent stem cell-derived model of the post-implantation human embryo
BDNF
Nuhu-Soso L, Denton H, Goffin DL, Hahn I and Evans GJO.
Neuronal differentiation enhances a cytoplasmic pool of tousled-like kinase 2 (TLK2)
Buchner F, Dokuzluoglu Z, Thomas J et al.
Synchronous 3D patterning of diverse CNS progenitors generates motor neurons of broad axial identity
Chen HJC, Yang A, Mazzaferro S et al.
Profiling human hypothalamic neurons reveals a candidate combination drug therapy for weight loss
Page T, Musi CA, Bakker SE et al.
Parkinson’s associated protein DJ-1 regulates intercellular communication via extracellular vesicles in oxidative stress
Pivoňková H, Sitnikov S, Kamen Y et al.
Heterogeneity in oligodendrocyte precursor cell proliferation is dynamic and driven by passive bioelectrical properties
Macarelli V, Harding EC, Gershlick DC, Merkle FT.
A short sequence targets transmembrane proteins to primary cilia
Agarwal D et al.
Human retinal ganglion cell neurons generated by synchronous BMP inhibition and transcription factor mediated reprogramming.
Agarwal D & Wahlin K
Differentiation of RGC Induced Neurons (RGC-iNs).
BMP-2
Huang TC, Wang YF, Vazquez-Ferrer E et al.
Sex-specific chromatin remodelling safeguards transcription in germ cells
Tan J, Virtue S, Norris DM et al.
Limited oxygen in standard cell culture alters metabolism and function of differentiated cells
Luo L, Foster NC, Man KL et al.
Hydrostatic pressure promotes chondrogenic differentiation and microvesicle release from human embryonic and bone marrow stem cells
Stucchi S, Sepulveda-Rincon LP, Dion C et al.
High resolution multi-scale profiling of embryonic germ cell-like cells derivation reveals pluripotent state transitions in humans
Yimiti D, Uchibe K, Toriyama M et al.
CD1530, selective RARγ agonist, facilitates Achilles tendon healing by modulating the healing environment including less chondrification in a mouse model
BMP-4
Barbieri E and Chambers I
OTX2 controls chromatin accessibility to direct somatic versus germline differentiation
Azami T, Theeuwes B, Ton M-LN et al.
STAT3 signalling enhances tissue expansion during postimplantation mouse development
Balmas E, Ratto ML, Snijders KE et al.
Single Cell Transcriptional Perturbome in Pluripotent Stem Cell Models
Truszkowski L, Bottini S, Bianchi S et al.
Refined home-brew media for cost-effective, weekend-free hiPSC culture and genetic engineering
Used:
- Recombinant human activin A protein (Qk001)
- Recombinant human FGF-2 (145 aa) protein (Qk025)
- Recombinant human FGF-2 (154 aa) protein (Qk027)
- Recombinant human BMP-4 protein (Qk038)
- Recombinant human NRG-1 protein (Qk045)
- Recombinant FGF2-G3 (145 aa) protein (Qk052)
- Recombinant FGF2-G3 (154 aa) protein (Qk053)
- Recombinant human TGF-β3 protein (Qk054)
- Recombinant human TGF-β1 PLUS™ protein (Qk010)

Cell therapy is becoming a possibility for many previously untreatable conditions, and it should be accessible to everyone. Creating a cost-effective, reliable and reproducible way of culturing human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) in a range of research labs, and allowing large scale culture for gene-editing purposes takes us one step closer to this.
Using high potency thermostable Qkine 145 amino acid FGF-G3 reduce FGF-2 use 8-fold and for weekend-free culture reduced media use by 57%. This makes hiPSCs a more accessible model for many labs doing basic and translational research.
Drozd AM, Mariani L, Guo X, Goitea V, Menezes NA and Ferretti E.
Progesterone Receptor Modulates Extraembryonic Mesoderm and Cardiac progenitor Specification during Mouse Gastrulation
Stucchi S, Sepulveda-Rincon LP, Dion C et al.
High resolution multi-scale profiling of embryonic germ cell-like cells derivation reveals pluripotent state transitions in humans
EGF
Żylicz J, van Nerum K, Wenzel A et al.
Metabolic rewiring underpins human trophoblast induction
Darrigrand J-F, Isaacson A and Spagnoli FM
Generation of human iPSC-derived pancreatic organoids to study pancreas development and disease
Rossignoli G, Oberhuemer M, Brun IS et al.
Feeder-free culture of naive human pluripotent stem cells retaining embryonic, extraembryonic and blastoid generation potential
FGF-10
Iyer DP, Khoei HH, van der Weijden VA et al.
mTOR activity paces human blastocyst stage developmental progression
Agarwal R, Dittmar T, Beer HD et al.
Human epidermis organotypic cultures, a reproducible system recapitulating the epidermis in vitro
Darrigrand J-F, Isaacson A and Spagnoli FM
Generation of human iPSC-derived pancreatic organoids to study pancreas development and disease
FGF-2
Huang, T et al.
Inhibition of PRC2 enables self-renewal of blastoid-competent naive pluripotent stem cells from chimpanzee
Zorzan I, Pellegrini M, Arboit M et al.
The transcriptional regulator ZNF398 mediates pluripotency and epithelial character downstream of TGF-beta in human PSCs
Buchner F, Dokuzluoglu Z, Thomas J et al.
Synchronous 3D patterning of diverse CNS progenitors generates motor neurons of broad axial identity
Meek S, Watson T, Eory L et al.
Stem cell-derived porcine macrophages as a new platform for studying host-pathogen interactions
Balmas E, Ratto ML, Snijders KE et al.
Single Cell Transcriptional Perturbome in Pluripotent Stem Cell Models
Truszkowski L, Bottini S, Bianchi S et al.
Refined home-brew media for cost-effective, weekend-free hiPSC culture and genetic engineering
Used:
- Recombinant human activin A protein (Qk001)
- Recombinant human FGF-2 (145 aa) protein (Qk025)
- Recombinant human FGF-2 (154 aa) protein (Qk027)
- Recombinant human BMP-4 protein (Qk038)
- Recombinant human NRG-1 protein (Qk045)
- Recombinant FGF2-G3 (145 aa) protein (Qk052)
- Recombinant FGF2-G3 (154 aa) protein (Qk053)
- Recombinant human TGF-β3 protein (Qk054)
- Recombinant human TGF-β1 PLUS™ protein (Qk010)

Cell therapy is becoming a possibility for many previously untreatable conditions, and it should be accessible to everyone. Creating a cost-effective, reliable and reproducible way of culturing human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) in a range of research labs, and allowing large scale culture for gene-editing purposes takes us one step closer to this.
Using high potency thermostable Qkine 145 amino acid FGF-G3 reduce FGF-2 use 8-fold and for weekend-free culture reduced media use by 57%. This makes hiPSCs a more accessible model for many labs doing basic and translational research.
Rosa VS, Sato N and Shahbazi MN et al.
Protocol for generating a 3D culture of epiblast stem cells
Drozd AM, Mariani L, Guo X, Goitea V, Menezes NA and Ferretti E.
Progesterone Receptor Modulates Extraembryonic Mesoderm and Cardiac progenitor Specification during Mouse Gastrulation
Page T, Musi CA, Bakker SE et al.
Parkinson’s associated protein DJ-1 regulates intercellular communication via extracellular vesicles in oxidative stress
Tan J, Virtue S, Norris DM et al.
Oxygen is a critical regulator of cellular metabolism and function in cell culture
Iyer DP, Khoei HH, van der Weijden VA et al.
mTOR activity paces human blastocyst stage developmental progression
Beltran-Rendon C, Price CJ, Glen K et al.
Modeling the selective growth advantage of genetically variant human pluripotent stem cells to identify opportunities for manufacturing process control
Tan J, Virtue S, Norris DM et al.
Limited oxygen in standard cell culture alters metabolism and function of differentiated cells
Arboit M, Zorzan I, Pellegrini M et al.
KLF7 is a general inducer of human pluripotency
GDF-15
Fejzo M, Rocha N, Cimino I et al.
GDF15 linked to maternal risk of nausea and vomiting during pregnancy
Fejzo M et al.
Fetally-encoded GDF15 and maternal GDF15 sensitivity are major determinants of nausea and vomiting in human pregnancy
Jeromson S, Akcan M, Baranowski B, Arbeau M, Bellucci A, Wright DC.
Daily GDF15 treatment has sex‐specific effects on body weight and food intake and does not enhance the effects of voluntary physical activity in mice
Cimino I, Kim H, Tung YCL et al.
Activation of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis by exogenous and endogenous GDF15
GDNF
Buchner F, Dokuzluoglu Z, Thomas J et al.
Synchronous 3D patterning of diverse CNS progenitors generates motor neurons of broad axial identity
Page T, Musi CA, Bakker SE et al.
Parkinson’s associated protein DJ-1 regulates intercellular communication via extracellular vesicles in oxidative stress
Agarwal D et al.
Human retinal ganglion cell neurons generated by synchronous BMP inhibition and transcription factor mediated reprogramming.
Agarwal D & Wahlin K
Differentiation of RGC Induced Neurons (RGC-iNs).
Gremlin
Sato N, Rosa VS, Makhlouf A et al.
Basal delamination during mouse gastrulation primes pluripotent cells for differentiation
HGF
Iyer DP, Khoei HH, van der Weijden VA et al.
mTOR activity paces human blastocyst stage developmental progression
KGF (FGF-7)
Darrigrand J-F, Isaacson A and Spagnoli FM
Generation of human iPSC-derived pancreatic organoids to study pancreas development and disease
LIF
Huang, T et al.
Inhibition of PRC2 enables self-renewal of blastoid-competent naive pluripotent stem cells from chimpanzee
Dinarello A, Betto RM, Diamante L et al.
STAT3 and HIF1α cooperatively mediate the transcriptional and physiological responses to hypoxia
Guo M, Wu J, Chen C et al.
Self-renewing human naïve pluripotent stem cells dedifferentiate in 3D culture and form blastoids spontaneously
From the lab of José Silva, Guangzhou Laboratory

A huge challenge in understanding human early embryo cell fate is due to limited access and ethical concerns. Recent research, however, from José C. R. Silva’s lab at Guangzhou National Laboratory, drawing from single-cell sequencing, suggests a conserved lineage specification process between human and mouse embryos. Blastoids, emerging models for early embryo development, generated solely from hnPSCs, offer insights into blastocyst formation without altering culture conditions. Self-renewing human naïve pluripotent stem cells (hnPSCs) spontaneously form blastoids in 3D culture, mimicking early human blastocysts. This process, mediated by the GSK3 inhibitor IM-12 in 5iLAF medium, involves upregulation of oxidative phosphorylation genes. hnPSCs dedifferentiate into E5 embryo-like intermediates, expressing SOX2/OCT4 and GATA6, which specify trophoblast fate by day 3, coinciding with blastoid formation. This was a fantastic paper to read as it is clear how this spontaneous blastoid formation highlights the importance of culture conditions and provides a new platform to study human embryo development in vitro, potentially reshaping our understanding of hnPSCs and embryo development.
Li H, Chang L, Huang J and Silva JCR.
Protocol for generating mouse morula-like cells resembling 8- to 16-cell stage embryo cells
Rosa VS, Sato N and Shahbazi MN et al.
Protocol for generating a 3D culture of epiblast stem cells
Drozd AM, Mariani L, Guo X, Goitea V, Menezes NA and Ferretti E.
Progesterone Receptor Modulates Extraembryonic Mesoderm and Cardiac progenitor Specification during Mouse Gastrulation
Krammer T and Tanaka EM
Neural tube organoid generation: a robust and reproducible protocol from single mouse embryonic stem cells
Hennessy MJ, Fulton T, Turner DA and Steventon B
Negative feedback on Retinoic Acid by Brachyury guides gastruloid symmetry-breaking
Borkowska M, Leitch HG.
Mouse Primordial Germ Cells: In Vitro Culture and Conversion to Pluripotent Stem Cell Lines
Krammer T, Stuart HT, Gromberg E et al.
Mouse neural tube organoids self-organize floorplate through BMP-mediated cluster competition
Żylicz J, van Nerum K, Wenzel A et al.
Metabolic rewiring underpins human trophoblast induction
Arboit M, Zorzan I, Pellegrini M et al.
KLF7 is a general inducer of human pluripotency
Klobučar T, Novljan J, Iosub IA at el.
Integrative analysis of higher-order transcriptome organisation and RNA condensation principles
Ferlazzo GM, Gambetta AM, Amato S et al.
Genome-wide screening in pluripotent cells identifies Mtf1 as a suppressor of mutant huntingtin toxicity
Heidari Khoei H, Javali A, Kagawa H et al.
Generating human blastoids modeling blastocyst-stage embryos and implantation
Noggin
Lumibao JC, Okhovat SR, Peck KL et al.
The effect of extracellular matrix on the precision medicine utility of pancreatic cancer patient-derived organoids
Bergmann S, Penfold CA, Slatery E et al.
Spatial profiling of early primate gastrulation in utero
Osorio-Vasquez V, Lumibao JC, Peck KL et al.
Identification of molecular and functional subtypes using chronic pancreatitis patient-derived organoid models
Agarwal R, Dittmar T, Beer HD et al.
Human epidermis organotypic cultures, a reproducible system recapitulating the epidermis in vitro
Feofanov M, Daubner GM, Saltalamacchia A et al.
Discovery and optimization of a guanylhydrazone-based small molecule to replace bFGF for cell culture applications
NRG-1
Truszkowski L, Bottini S, Bianchi S et al.
Refined home-brew media for cost-effective, weekend-free hiPSC culture and genetic engineering
Used:
- Recombinant human activin A protein (Qk001)
- Recombinant human FGF-2 (145 aa) protein (Qk025)
- Recombinant human FGF-2 (154 aa) protein (Qk027)
- Recombinant human BMP-4 protein (Qk038)
- Recombinant human NRG-1 protein (Qk045)
- Recombinant FGF2-G3 (145 aa) protein (Qk052)
- Recombinant FGF2-G3 (154 aa) protein (Qk053)
- Recombinant human TGF-β3 protein (Qk054)
- Recombinant human TGF-β1 PLUS™ protein (Qk010)

Cell therapy is becoming a possibility for many previously untreatable conditions, and it should be accessible to everyone. Creating a cost-effective, reliable and reproducible way of culturing human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) in a range of research labs, and allowing large scale culture for gene-editing purposes takes us one step closer to this.
Using high potency thermostable Qkine 145 amino acid FGF-G3 reduce FGF-2 use 8-fold and for weekend-free culture reduced media use by 57%. This makes hiPSCs a more accessible model for many labs doing basic and translational research.
NT-3
Liu Y, Li X, Xu H et al.
Spinal cord stimulation induces Neurotrophin-3 to improve diabetic foot disease
Qkine
Barber L, Spicer C.
The effect of pyridinecarboxaldehyde functionalisation on reactivity and N-terminal protein modification
Karusheva Y, Ratcliff M, Mörseburg A et al.
The Common H202D Variant in GDF-15 Does Not Affect Its Bioactivity but Can Significantly Interfere with Measurement of Its Circulating Levels
Barber LJ, Yates NDJ, Fascione MA et al.
Selectivity and stability of N-terminal targeting protein modification chemistries
Venkatesan M, Semper C, Skrivergaard S et al.
Recombinant production of growth factors for application in cell culture
R-spondin
Lumibao JC, Okhovat SR, Peck KL et al.
The effect of extracellular matrix on the precision medicine utility of pancreatic cancer patient-derived organoids
Ku B, Eisenbarth D, Baek S et al.
PRMT1 promotes pancreatic cancer development and resistance to chemotherapy
Marsee A, Ritchie A, Myszczyszyn A et al.
Mass Generation and Long-term Expansion of Hepatobiliary Organoids from Adult Primary Human Hepatocytes
Osorio-Vasquez V, Lumibao JC, Peck KL et al.
Identification of molecular and functional subtypes using chronic pancreatitis patient-derived organoid models
Agarwal R, Dittmar T, Beer HD et al.
Human epidermis organotypic cultures, a reproducible system recapitulating the epidermis in vitro
Choi W, Kim YH, Woo SM et al.
Establishment of Patient-Derived Organoids Using Ascitic or Pleural Fluid from Cancer Patients
Feofanov M, Daubner GM, Saltalamacchia A et al.
Discovery and optimization of a guanylhydrazone-based small molecule to replace bFGF for cell culture applications
SCF
Azami T, Theeuwes B, Ton M-LN et al.
STAT3 signalling enhances tissue expansion during postimplantation mouse development
TGF-β
Shin D, Kim CN, Ross J et al.
Thalamocortical organoids enable in vitro modeling of 22q11.2 microdeletion associated with neuropsychiatric disorders
Truszkowski L, Bottini S, Bianchi S et al.
Refined home-brew media for cost-effective, weekend-free hiPSC culture and genetic engineering
Used:
- Recombinant human activin A protein (Qk001)
- Recombinant human FGF-2 (145 aa) protein (Qk025)
- Recombinant human FGF-2 (154 aa) protein (Qk027)
- Recombinant human BMP-4 protein (Qk038)
- Recombinant human NRG-1 protein (Qk045)
- Recombinant FGF2-G3 (145 aa) protein (Qk052)
- Recombinant FGF2-G3 (154 aa) protein (Qk053)
- Recombinant human TGF-β3 protein (Qk054)
- Recombinant human TGF-β1 PLUS™ protein (Qk010)

Cell therapy is becoming a possibility for many previously untreatable conditions, and it should be accessible to everyone. Creating a cost-effective, reliable and reproducible way of culturing human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) in a range of research labs, and allowing large scale culture for gene-editing purposes takes us one step closer to this.
Using high potency thermostable Qkine 145 amino acid FGF-G3 reduce FGF-2 use 8-fold and for weekend-free culture reduced media use by 57%. This makes hiPSCs a more accessible model for many labs doing basic and translational research.