Currency
Recombinant human VEGF165 protein (Qk048)
Recombinant human vascular endothelial growth factor 165 (VEGF165/ VEGF-165/ VEGF165) protein is widely used in culturing primary endothelial cells, such as human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC).
VEGF165 is commonly used with human-induced pluripotent stem cells or embryonic stem cells-derived endothelial cells for developing human vascular tissue models. It has many applications including its use in neural research involving oligodendrocyte precursor cells, Schwann cells, astrocytes, and microglia. It plays a role in bone formation, regulates mesenchymal stem cell differentiation, and serves as a survival factor for chondrocytes, hematopoietic stem cells, and tumor cells.
Qkine recombinant human VEGF165 protein is a highly pure and potent 38 kDa homodimer, disulfide-linked consisting of two 165 amino acid polypeptide chains. It is an animal origin-free (AOF) and carrier protein-free (CF).
Orders are typically shipped same or next day (except Friday).
Easy world-wide ordering, direct or through our distributors.
1000µg will be despatched as 2 x 500µg
Fast and free shipping.
Buy online with secure credit card or purchase order.
For any questions, please email orders@qkine.com
Summary
High purity human VEGF165 (Uniprot: P15692)
>98%, by SDS-PAGE quantitative densitometry
38.3 kDa (dimer), 19 kDa monomer
- Expressed in E. coli
Animal origin-free (AOF) and carrier protein-free
Manufactured in Cambridge, UK
- Lyophilized from acetonitrile/TFA
- Resuspend in water at >100 µg/ml, prepare single use aliquots, add carrier protein if desired and store frozen at -20 oC (short-term) or -80 oC (long-term)
Featured applications
Angiogenic cell research
- Endothelial cell differentiation
- Vasculature in organoids
- Neural stem cells research
- Mesenchymal stem cells research
- hPSC-derived mesoderm differentiation
Human
Frequently used together
Recombinant human BMP-4 protein (Qk038)
Recombinant FGF2-G3 145 aa protein (Qk052)
Recombinant FGF2-G3 protein (Qk053)
Recombinant human FGF-2 (bFGF) 145 aa protein (Qk025)
Recombinant human FGF-2 (bFGF) 154 aa protein (Qk027)
Recombinant human EGF protein (Qk011)
Recombinant human PDGF-AA protein (Qk043)
Recombinant human PDGF-BB protein (Qk044)
Bioactivity
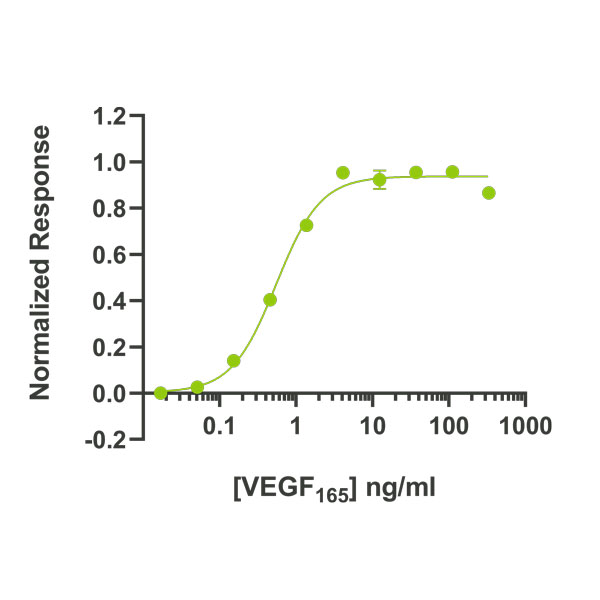
The bioactivity of QK048 is measured using a luciferase reporter cell line which stably expresses the KDR (VEGFR-2) receptor. Cells were incubated with different concentrations of VEGF165 for 6 hours before assaying for luciferase production. EC50=0.55 ng/ml (14.4 pM), data from Qk048 lot #104393, n=3.
Purity
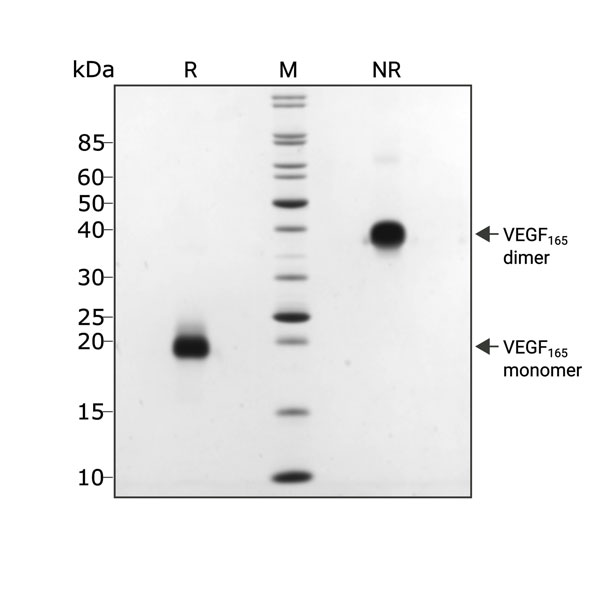
Human VEGF165 (Qk048) migrates as a dimer at 38 kDa in non-reducing (NR) conditions and as a monomer at 19 kDa upon reduction (R). No contaminating bands are visible. Purified recombinant protein (3 µg) was resolved using 15% w/v SDS-PAGE in reduced (+β-mercaptoethanol, R) and non-reduced (-β-mercaptoethanol, NR) conditions and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250. Data from Qk048 lot #104393.
Further quality assays
Mass spectrometry: single species with expected mass
Endotoxin: <0.005 EU/μg protein (below level of detection)
Recovery from stock vial: >95%
We are a company founded and run by scientists to provide a service and support innovation in stem cell biology and regenerative medicine. All our products are exceptionally high purity, with complete characterisation and bioactivity analysis on every lot.
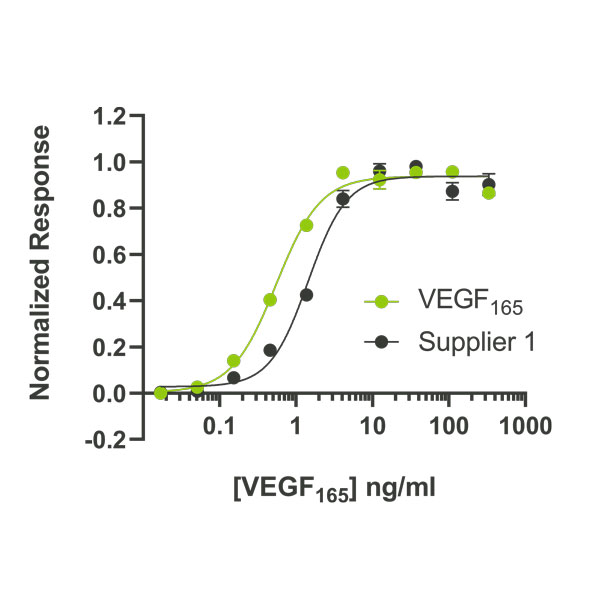
Comparison with other suppliers
Qkine VEGF165 has higher bioactivity than an alternative supplier.
The bioactivity of Qkine and an alternative supplier were compared directly using a luciferase reporter cell line which stably expresses the KDR (VEGFR-2) receptor. Cells were incubated with different concentrations of VEGF165 for 6 hours before assaying for luciferase production.
EC50=0.55 ng/ml (14.4 pM) for Qk048, data from Qk048 lot #104393, n=3
EC50=1.44 ng/ml (37.6 pM) for Supplier 1 VEGF165, , n=3
Protein background
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a member of the platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) family and a core regulator of angiogenesis and vascular permeability [1,2]. It is responsible for the survival, proliferation, migration, and specialization of endothelial cells, thus called an endothelial cell surviving factor [2,3].
In humans, VEGF is produced as multiple alternately spliced isoforms indicating the number of amino acids in length: VEGF121, VEGF145, VEGF148, VEGF162, VEGF165a, VEGF165b, VEGF183, VEGF189, and VEGF206. VEGF165 (or VEGF165a) is the most abundantly expressed isoform composed of 165 amino acids [1].
VEGF165 signals through the type I transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinases VEGFR1 (also called Flt-1) and VEGFR2 (Flk-1/KDR) [2]. Some VEGF family members (including VEGFA 165) also bind to the co-receptors neuropilin 1 (NRP1) and neuropilin 2 (NRP2), which can stimulate VEGFR2 activation. It is characterized by the presence of eight conserved cysteine residues forming a receptor-binding cystine-knot structure [4,5].
VEGF is widely used in culturing primary endothelial cells, such as human umbilical vein endothelial cells, under serum-free conditions for blood vessel developmental studies. VEGF165 is commonly used with human-induced pluripotent stem cells or embryonic stem cells-derived endothelial cells for developing human vascular tissue models for disease mechanism studies. Immunocytochemical staining with CD31 expression marker is used to indicate the presence of endothelial cells, thereby suggesting successful endothelial cell differentiation [6,7]. Endothelial cells can also be derived from hair follicle stem cells [8].
In addition to its angiogenic role, it is also involved in promoting neurogenesis and stimulating neural stem cell proliferation [9,10]. It can promote the proliferation, survival or migration of other glial cells such as oligodendrocyte precursor cells, Schwann cells, and can stimulate the expression of trophic factors by astrocytes [11]. Moreover, it is a critical factor in generating human pluripotent stem cell-derived vascularized brain organoids [6].
Finally, VEGF also plays a role in bone formation and regulates mesenchymal stem cell differentiation of pluripotent stem cells and bone marrow stem cells [12,13]. Therefore, it serves as a survival factor for chondrocytes, hematopoietic stem cells, and tumor cells [12,14].
The strong implications of VEGF have led to preclinical studies on the potential of VEGF administration in neurodegenerative and ischemic diseases [1,2,11]. The inhibition of VEGF has been approved for the treatment of neovascular ocular disease to prevent the blood brain barrier breakdown or excessive angiogenesis11. It is also a target in anti-angiogenic strategies in cancer due to its contribution in tumor angiogenesis [2,14].
FAQ
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor 165 is a specific isoform of the vascular endothelial growth factor family. It stimulates vascular permeability plays a crucial role in various embryonic development, wound healing, and tumor angiogenesis.
VEGF165 stimulates angiogenesis by stimulating the proliferation of endothelial cells. It is also involved in the regulation and differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into endothelial cells, neural stem cells, and hematopoietic stem cells.
Angiogenesis is the process by which new blood vessels are formed. It is a critical part of embryonic development, growth, and wound healing. It is regulated by pro-angiogenic factors such as VEGF acting on endothelial cells, cells lining the interior of blood vessels.
VEGF165 and VEGF121 are two different alternatively spliced isoforms of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) protein. VEGF165 and VEGF121 are composed of 165 and 121 amino acids respectively.
VEGF165 binds to the VEGF receptor tyrosine kinases, known as VEGFR-1 (Flt-1) and VEGFR-2 (KDR/Flk-1) on endothelial cells.
Our products are for research use only and not for diagnostic or therapeutic use. Products are not for resale.


What others are saying
There are no contributions yet.