Currency
Recombinant human FGF-18 protein (Qk069)
Fibroblast Growth Factor 18 (FGF-18), a member of the FGF family, characterized by its heparin-binding properties plays a significant role in regulating diverse biological processes such as embryonic development, skeletal and bone development, cartilage maintenance, angiogenesis and tissue repair.
In cell culture, FGF18 is widely used to support cell culture maintenance and proliferation, promote chondrogenic and osteogenic differentiation of stem cells, stimulate angiogenesis, and enhance tissue regeneration.
FGF-18 is a high purity truncated protein with a molecular weight of 20.2 kDa. This protein is carrier-free and tag-free to ensure its purity with exceptional lot-to-lot consistency. Qkine Fibroblast Growth Factor 18 is suitable for the culture of reproducible and high-quality stem cells, primary cells and other relevant cells.
Orders are typically shipped same or next day (except Friday).
Easy world-wide ordering, direct or through our distributors.
1000µg will be despatched as 2 x 500µg
Fast and free shipping.
Buy online with secure credit card or purchase order.
For any questions, please email orders@qkine.com
Summary
High purity human protein (Uniprot number: O76093)
>98%, by SDS-PAGE quantitative densitometry
Source: Expressed in E. coli
Size in 20.2 kDa monomer
Animal origin-free (AOF) and carrier protein-free
Manufactured in Cambridge, UK
Lyophilized from Tris/NaCl
Resuspend in water at >100 µg/mL, prepare single-use aliquots, add carrier protein if desired, and store frozen at -20°C or -80°C.
Featured applications
Growth and proliferation of chondrocytes, fibroblasts and primary cells
Culture of mesenchymal, embryonic and pluripotent stem cells
Directed chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells
Directed osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells
Stimulation of angiogenesis and vascular network development
Induction of cell migration, proliferation and extracellular matrix production
zFGF5
Fibroblast growth factor 18
Human
Frequently used together
Recombinant human FGF-2 145aa protein (Qk0025)
Recombinant human FGF-2 154aa protein (Qk027)
Recombinant FGF2-G3 protein (Qk053)
Recombinant human FGF-9 protein (Qk039)
Recombinant human BMP-4 protein (Qk038)
Recombinant hunam BMP-2 protein Qk007
Recombinant human TGF-ß1 PLUS protein (Qk010)
Recombinant human TGF-ß3 protein (Qk054)
Recombinant human IGF-1 protein (Qk047)
Recombinant human VEGF165 protein (Qk048)
Recombinant human PDGF-AA protein (Qk043)
Recombinant human PDGF-BB protein (Qk044)
Recombinant human EGF protein (Qk011)
Recombinant human HGF protein (Qk013)
Bioactivity
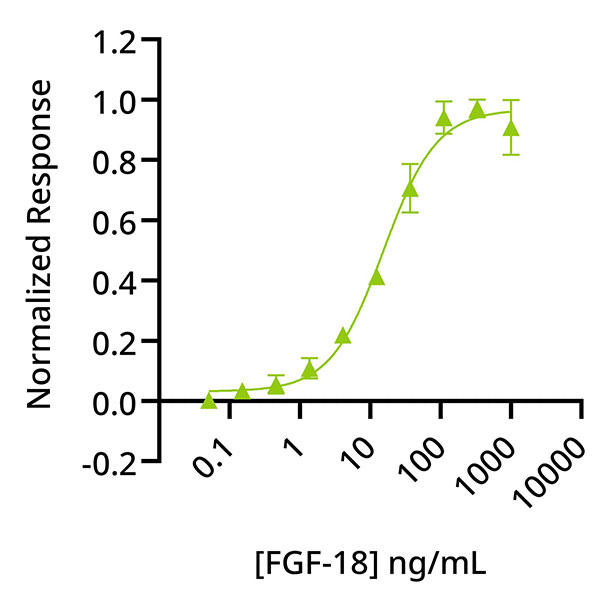
Recombinant FGF-18 activity is determined using FGF-18-responsive luciferase assay. Transfected HEK293 cells are treated in triplicate with a serial dilution of FGF-18 for 3 hours. Firefly activity is measured and normalised to the control Renilla luciferase activity. Data from Qk069 lot 204634.
EC50 = 15.5 ng/mL (0.77 nM)
Purity
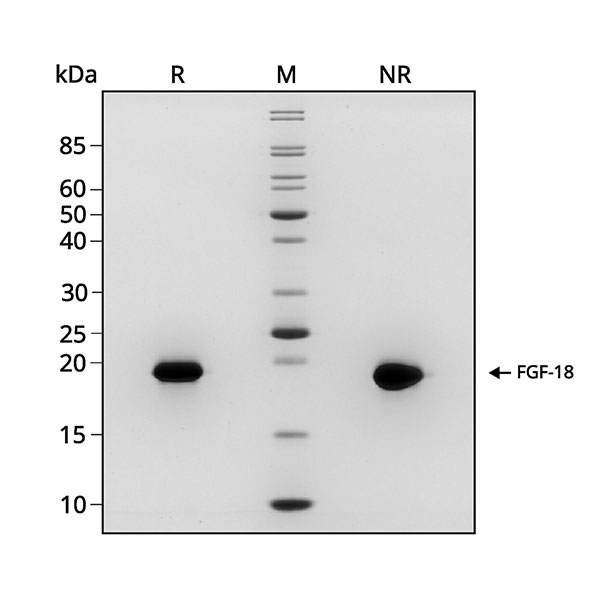
Recombinant FGF-18 migrates as a band at approximately 20 kDa (monomer) in reduced (R) and non-reduced (NR) conditions. No contaminating protein bands are present.
The purified recombinant protein (3 µg) was resolved using 15% w/v SDS-PAGE in reduced (+β-mercaptoethanol, R) and non-reduced (NR) conditions and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250. Data from Qk069 lot #204634.
Further quality assays
Mass spectrometry, single species with the expected mass
Endotoxin: <0.005 EU/μg protein (below the level of detection)
Recovery from stock vial: >95%
We are a company founded and run by scientists to provide a service and support innovation in stem cell biology and regenerative medicine. All our products are exceptionally high purity, with complete characterisation and bioactivity analysis on every lot.
Protein background
Fibroblast Growth Factor 18 (FGF-18), a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family is characterized by its heparin-binding properties and involved in diverse biological processes such as embryonic development, tissue repair, and cellular regulation [1]. FGF18 is normally expressed in adult tissues undergoing regeneration and plays crucial roles in skeletal development and repair [2], highlighting its importance in tissue homeostasis and repair mechanisms.
Specifically, FGF-18 exerts significant effects on skeletal biology by regulating endochondral bone formation, chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation, and osteogenesis [3]. It also contributes to cartilage maintenance by promoting articular chondrocyte proliferation and integrity in joints [4]. Additionally, FGF-18 participates in angiogenesis, promoting new blood vessel formation during tissue repair [5], and has demonstrated benefits in wound healing by enhancing cell proliferation, migration, and extracellular matrix production [4].
Beyond its roles in skeletal development, cartilage maintenance and tissue repair, FGF18 has significant implications in cell culture systems. FGF-18 is a potent mitogen that stimulates cell proliferation and activates intracellular signaling pathways like MAPK and PI3K-Akt, crucial for cell growth and survival [6]. FGF-18 serves as a supplement in growth media to support primary cell expansion, including chondrocytes and fibroblasts while also maintaining and directing the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) [7-9,16]. Combined with other growth factors, FGF-18 helps sustain the undifferentiated state of stem cells and prevents spontaneous differentiation.
Furthermore, FGF18 plays a pivotal role in regulating chondrogenesis and osteogenesis, enhancing the differentiation of mesenchymal progenitor cells into chondrocytes and osteoblasts, crucial for cartilage and bone formation [3,7-8]. Recent studies have also highlighted the role of FGF-18 in other processes such as a role in lung organogenesis by promoting lunch branching morphogenesis using mesenchymal progenitor cells [14], induction of liver fibrosis through hepatic stellate cells [15]. Its angiogenic properties facilitate endothelial cell proliferation and migration, aiding in the development of functional vascular networks in tissue engineering applications [4].
Structurally, FGF-18 shares common features with other FGFs, consisting of a core domain responsible for binding to FGF receptors (FGFRs), particularly FGFR1c, FGFR2c, FGFR3c and FGFR4 and heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs), essential for ligand-receptor interaction and subsequent signal transduction. Upon binding to specific FGFRs like FGFR3 and FGFR4, FGF-18 triggers receptor dimerization and activates downstream signaling pathways, notably Ras-MAPK and PI3K-Akt, regulating diverse biological processes [3, 10-13].
Due to its roles in tissue repair and regeneration, FGF18 is being explored as a potential therapeutic agent for musculoskeletal disorders such as osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, and bone fractures [9]. Early studies and trials have investigated FGF-18-based therapies to promote cartilage repair and bone regeneration, underscoring its therapeutic potential pending further research into efficacy and safety in clinical settings [9].
In summary, FGF-18 is a multifunctional growth factor pivotal in skeletal development, cartilage maintenance, angiogenesis, and tissue repair. Its diverse biological functions make it a promising candidate for therapeutic interventions targeting tissue regeneration and treatment of musculoskeletal disorders.
1. Ornitz, D. M. & Itoh, N. [No title found]. Genome Biol 2, reviews3005.1 (2001).
2. Ohbayashi, N. et al. FGF18 is required for normal cell proliferation and differentiation during osteogenesis and chondrogenesis. Genes Dev. 16, 870–879 (2002).
3. Liu, Z., Xu, J., Colvin, J. S. & Ornitz, D. M. Coordination of chondrogenesis and osteogenesis by fibroblast growth factor 18. Genes Dev. 16, 859–869 (2002).
4. Davidson, D. et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) 18 Signals through FGF Receptor 3 to Promote Chondrogenesis. Journal of Biological Chemistry 280, 20509–20515 (2005).
5. Tomanek, R. J. et al. Embryonic coronary vasculogenesis and angiogenesis are regulated by interactions between multiple FGFs and VEGF and are influenced by mesenchymal stem cells. Developmental Dynamics 239, 3182–3191 (2010).
6. Ornitz, D. M. & Itoh, N. The Fibroblast Growth Factor signaling pathway. WIREs Developmental Biology 4, 215–266 (2015).
7. Shu, C., Smith, S. M., Little, C. B. & Melrose, J. Use of FGF-2 and FGF-18 to direct bone marrow stromal stem cells to chondrogenic and osteogenic lineages. Future Science OA 2, FSO142 (2016).
8. Huang, L. et al. Synergistic Effects of FGF-18 and TGF- β 3 on the Chondrogenesis of Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Pellet Culture. Stem Cells International 2018, 1–10 (2018).
9. Zhang, W., Ouyang, H., Dass, C. R. & Xu, J. Current research on pharmacologic and regenerative therapies for osteoarthritis. Bone Res 4, 15040 (2016).
10. Liu, Z., Lavine, K. J., Hung, I. H. & Ornitz, D. M. FGF18 is required for early chondrocyte proliferation, hypertrophy and vascular invasion of the growth plate. Developmental Biology 302, 80–91 (2007).
11. Belgacemi, R. et al. Preferential FGF18/FGFR activity in pseudoglandular versus canalicular stage human lung fibroblasts. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 11, 1220002 (2023).
12. Zhang, J. et al. FGF18–FGFR2 signaling triggers the activation of c-Jun–YAP1 axis to promote carcinogenesis in a subgroup of gastric cancer patients and indicates translational potential. Oncogene 39, 6647–6663 (2020).
13. Yao, X. et al. Fibroblast growth factor 18 exerts anti-osteoarthritic effects through PI3K-AKT signaling and mitochondrial fusion and fission. Pharmacological Research 139, 314–324 (2019).
14. Danopoulos, S. et al. FGF18 promotes human lung branching morphogenesis through regulating mesenchymal progenitor cells. American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 324, L433–L444 (2023).
15. Tsuchiya, Y. et al. Fibroblast growth factor 18 stimulates the proliferation of hepatic stellate cells, thereby inducing liver fibrosis. Nat Commun 14, 6304 (2023).
16. Chen, X. et al. Integration Capacity of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cartilage. Tissue Engineering Part A 25, 437–445 (2019).
FAQ
FGF18 is a member of the FGF family of proteins that is involved in various biological processes, including embryonic development, tissue repair, and cellular regulation.
FGF-18 is found in various tissues including skeletal tissues such as cartilage, bone, and synovium. It is also expressed in tissues undergoing repair and regeneration.
FGF-18 is not classified as a cytokine but categorized as a growth factor.
FGF18 binds to fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs), particularly FGFR3 and FGFR4, as well as heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) on the cell surface triggering receptor dimerization and initiation of downstream signaling cascades.
The FGF-18 receptor allows the binding of FGF-18 protein and activation of various intracellular pathways such as Ras-MAPK (Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase) and PI3K (Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase)-Akt pathways to regulate cellular processes.
The FGF18 pathway involves binding of FGF-18 to its receptors (FGFRs), leading to receptor dimerization and activation of downstream signaling pathways to regulate various biological processes such as proliferation, differentiation, and survival.
In cell culture, FGF-18 is used as a growth media supplement to support the expansion and maintenance of various cell types, including mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), chondrocytes, and fibroblasts. It promotes cell proliferation, maintains stem cell pluripotency, and enhances differentiation when combined with other growth factors and signaling molecules.
Additional resources
Our products are for research use only and not for diagnostic or therapeutic use. Products are not for resale.


What others are saying
There are no contributions yet.