 Recombinant human GDNF protein (Qk051)
Recombinant human GDNF protein (Qk051)Recombinant human GDNF protein (Qk051)
Price range: £230.00 through £2,900.00
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) is a member of neurotrophin family and GDNF family of ligands (GFL). GDNF plays a crucial role in the development, growth, and survival of neurons in particular midbrain dopaminergic neurons. GNDF is used to maintain neurons and cortical organoids and to differentiate dopaminergic neurons from human pluripotent stem cell-derived neural progenitors. GDNF also facilitates the differentiation of neural progenitors to astrocytes.
Recombinant human GDNF bioactive 30 kDa homodimer. This protein is animal origin-free (AOF), carrier protein-free, and tag-free to ensure its purity with exceptional lot-to-lot consistency.
In stock
Orders are typically shipped same or next day (except Friday).
Easy world-wide ordering, direct or through our distributors.
Price range: £230.00 through £2,900.00
Fast and free shipping.
Buy online with secure credit card or purchase order. For any questions, please email orders@qkine.com
Summary:
- High purity GDNF (Uniprot: P39905)
- 30.4 kDa (dimer)
>98%, by SDS-PAGE quantitative densitometry
Expressed in E. coli
Animal origin-free (AOF) and carrier protein-free
Manufactured in our Cambridge, UK laboratories
Lyophilized from acetonitrile, TFA
- Resuspend in sterile-filtered water at >50 µg/ml, add carrier protein if desired, prepare single use aliquots and store frozen at -20 °C (short-term) or -80 °C (long-term).
Featured applications:
Differentiation of midbrain dopaminergic neurons
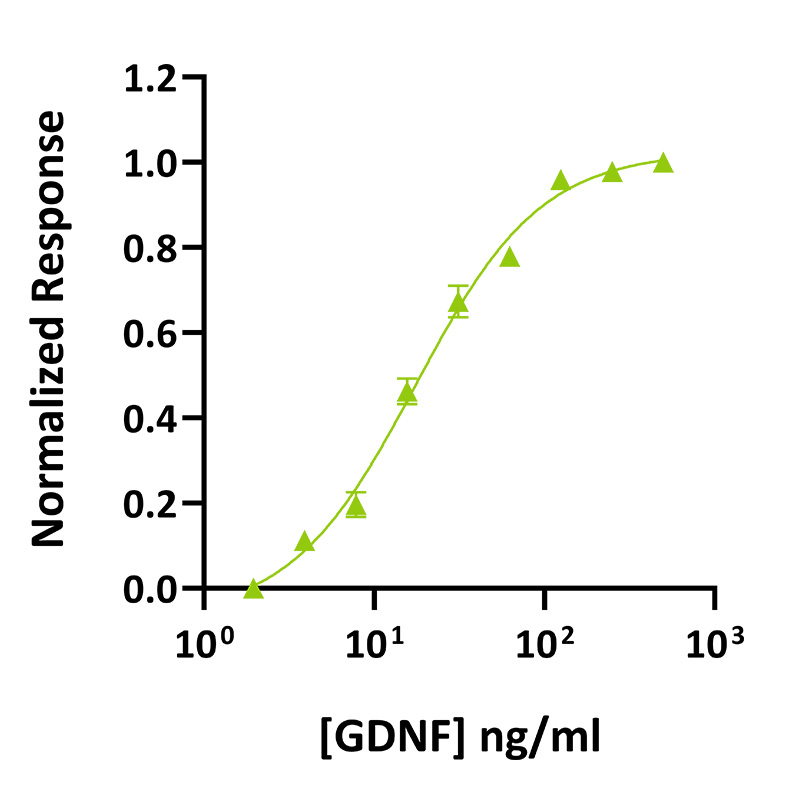
GDNF activity was determined using a SH-SY5Y cell proliferation assay. Cells were incubated with different concentrations of GDNF in the presence of retinoic acid and recombinant GFR α1 for 3 days before viable cell measurement using an MTS assay. Data are n=2. EC50 = 18 ng/ml. Data from Qk051 batch #104372.
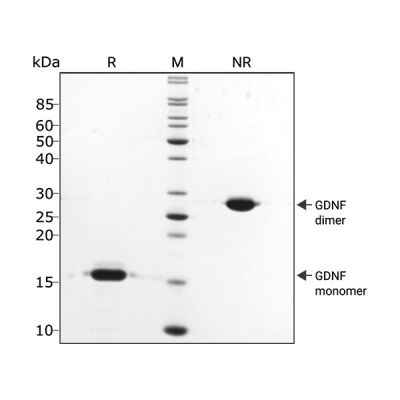
GDNF migrates as a single band at 30 kDa in non-reducing (NR) conditions and 15 kDa upon reduction (R). No contaminating protein bands are visible. Purified recombinant protein (3 µg) was resolved using 15% w/v SDS-PAGE in reduced (+β-mercaptothanol, R) and non-reduced (NR) conditions and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250. Data from Qk051 batch #104372.
Further quality assays
Mass spectrometry: single species with expected mass
Recovery from stock vial: >95%
Endotoxin: <0.005 EU/μg protein (below level of detection)
We are a company founded and run by scientists to provide a service and support innovation in stem cell biology and regenerative medicine. All our products are exceptionally high purity, with complete characterisation and bioactivity analysis on every lot.
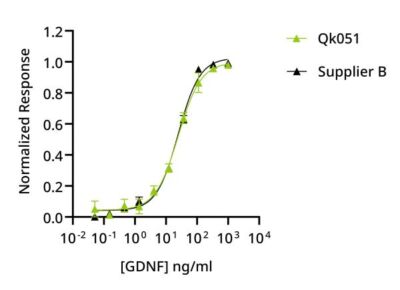
Qkine GDNF (Qk051) bioactivity was compared with an alternative supplier (Supplier 1) using a SH-SY5Y cell proliferation assay (as above). Qkine GDNF was found to have higher bioactivity than Supplier 1 GDNF. Qk051 EC50 = 18 ng/ml, Supplier 1 EC50 = 26 ng/ml, P = 0.018
Technote | GDNF (Qk051) bioactivityTechnote | GDNF (Qk051) stabilityProtein background
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) is a neurotrophic factor and a member of the GDNF family of ligands (GFL) which include neurturin, artemin, and persephin [1,2]. GFLs regulate several biological processes including cell survival, cell proliferation, cell differentiation, cell migration, and neurite outgrowth [1,3,4]. GDNF protein plays a crucial role in the development, growth, and survival of neurons in particular midbrain dopaminergic neurons [5]. It promotes the axon growth and innervation of dopamine neurons. It also facilitates the differentiation of neural progenitors to astrocytes and is involved in neuroprotection[6,7]. In addition, it is involved in kidney development and spermatogenesis [8,9].
In cell culture, GDNF supports the survival and growth of neurons and astrocytes. It is used in combination with other growth factors to differentiate human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neural progenitors into neurons and astrocytes. GDNF is used for the differentiation, survival, and maturation of dopaminergic neurons with brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), FGF-8a/FGF-8b, and Shh [10-13]. Glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons are obtained with combinations of BDNF, GDNF, NT-3, or insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) [14-16]. Also, the culture of cortical organoids requires BDNF and GDNF for maturation [17,18]. Finally, it can be used to generate and maintain astrocytes along with ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) and leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) [19-21].
GDNF is mainly produced and released by glial cells such as astrocytes, Schwann cells, and satellite cells [22]. It is a homodimer of a molecular weight of 30 kDa which belongs to the cystine-knot protein family [1,23]. The GFLs act as biologically active homodimers that signal through the transmembrane RET receptor tyrosine kinase [24]. GFL activation of RET is dependent upon co-receptors, namely the four GDNF Family Receptor α (GFRα1-4). GFL signalling specificity arises from the preferentially binding of each ligand to one of the four GFRα receptors; GDNF preferentially binds GFRα1 with high affinity [1,24].
GDNF has shown promise in various therapeutic applications neurodegenerative diseases and disorders such as Parkinson’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Huntington’s disease, peripheral nerve and spinal cord injuries [1,25]. The idea is to harness GDNF for clinical use to promote the survival and function of dopaminergic neurons, potentially slowing or reversing the progression of these diseases. Clinical trials using it has shown improved motor function in patients with Parkinson’s disease [26,27]. Finally, GDNF has also been proposed for the treatment of drug addiction and alcoholism [25].
Additional resources
- Technote | GDNF (Qk051) bioactivity
- Technote | GDNF (Qk051) stability
- Animal origin-free BDNF and GDNF neural growth factors for enhanced iPSC-derived neuronal cultures (PDF)
- Differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) into dopaminergic neurons (PDF)
- Stability of Qkine recombinant growth factors and cytokines in conditioned media (PDF)
- Poster: Neural and glial cell maintenance and differentiation
- Poster: Pluripotent stem-cell derived organoids
- Brochure: Growth factors for neural and glial cell differentiation
- Brochure: Growth factors for enhanced organoid culture protocols
Publications using Recombinant human GDNF protein (Qk051)
-
Human retinal ganglion cell neurons generated by synchronous BMP inhibition and transcription factor mediated reprogramming.
Agarwal D et al.
DOI: doi: 10.1038/s41536-023-00327-x -
Differentiation of RGC Induced Neurons (RGC-iNs).
Agarwal D & Wahlin K
DOI: dx.doi.org/10.17504/protocols.io.14egn2pqzg5d/v2 -
Parkinson’s associated protein DJ-1 regulates intercellular communication via extracellular vesicles in oxidative stress
Page T, Musi CA, Bakker SE et al.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-5669239/v1 -
Synchronous 3D patterning of diverse CNS progenitors generates motor neurons of broad axial identity
Buchner F, Dokuzluoglu Z, Thomas J et al.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.12.13.628384
FAQ
GDNF protein plays a crucial role in the development, growth, and survival of midbrain dopaminergic neurons.
GDNF is mainly released by glial cells such as astrocytes, Schwann cells, and satellite cells.
Neurotrophic factors (also known as neurotrophins) include Nerve Growth Factor (NGF), Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF), Glial-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (GDNF), Neurotrophin-3 (NT-3), and Neurotrophin-4/5 (NT-4/5).
GDNF has shown potential therapeutic applications for Parkinson’s disease. Clinical trials using it has shown improved motor function which could slow the progression of the disease.
GDNF is used as a growth factor which is supplemented in cell culture media to promote the differentiation, growth, and maturation of dopaminergic neurons.
NGF, GDNF, and BDNF are all part of the neurotrophins or neurotrophic factors family. They all regulate the development, growth, and survival of neurons and have more specific roles. NGF is associated with the growth and maintenance of sensory and sympathetic neurons. BDNF and GDNF are both associated with dopaminergic, glutamatergic, and GABAergic neurons. In addition, BDNF plays a crucial role in synapses formation whereas GDNF is involved in the growth and maintenance of other glial cells such as astrocytes.
GDNF protein plays a crucial role in the development, growth, and survival of midbrain dopaminergic neurons.
GDNF is mainly released by glial cells such as astrocytes, Schwann cells, and satellite cells.
Neurotrophic factors (also known as neurotrophins) include Nerve Growth Factor (NGF), Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF), Glial-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (GDNF), Neurotrophin-3 (NT-3), and Neurotrophin-4/5 (NT-4/5).
GDNF has shown potential therapeutic applications for Parkinson’s disease. Clinical trials using it has shown improved motor function which could slow the progression of the disease.
GDNF is used as a growth factor which is supplemented in cell culture media to promote the differentiation, growth, and maturation of dopaminergic neurons.
Neurotrophin proteins regulate neuronal growth and survival, neuroprotection, neurotransmitter release, synaptic function, and plasticity within the adult central and peripheral nervous system.
Neurotrophins promote the survival and growth of neurons by inhibiting apoptosis (programmed cell death) in a process called neuroprotection.
Our products are for research use only and not for diagnostic or therapeutic use. Products are not for resale.
What others are saying
Very happy with this product. My neuronal cultures look very healthy and there has been no difference in morphology or mechanism of the neurons since switching from a more expensive competitive brand. Our lab will be continuing to purchase.
hh495 - February 17, 2023

Receive an Amazon gift voucher when you leave us a review.
£25, $30 or €30 for reviews with an image and £10, $15 or €15 for reviews without an image
