 Recombinant human BDNF protein (Qk050)
Recombinant human BDNF protein (Qk050)Recombinant human BDNF protein (Qk050)
Price range: £230.00 through £2,900.00
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a member of neurotrophin family and plays a crucial role in neural development, maintenance, and function. It stimulates neurogenesis and is also a major regulator of synaptic plasticity and neuroprotection. It is used to maintain neurons and differentiate and mature human pluripotent stem cell-derived neural progenitors to cortical and motor neurons and cortical organoids.
Recombinant human BDNF protein has a molecular weight of 14 kDa. This protein is animal origin-free, carrier-free, tag-free, and non-glycosylated to ensure its purity with exceptional lot-to-lot consistency. Qk050 is suitable for the culture of reproducible and high-quality cortical and motor neurons and cortical organoids.
Qkine BDNF is also available as cell therapy grade with extended quality testing and documentation – Qk050-CTG
In stock
Orders are typically shipped same or next day (except Friday).
Easy world-wide ordering, direct or through our distributors.
Price range: £230.00 through £2,900.00
Buy online with secure credit card or purchase order. For any questions, please email orders@qkine.com
Summary:
- High purity human BDNF protein (Uniprot: P23560)
- dop
>98%, by SDS-PAGE quantitative densitometry
Expressed in E. coli
Animal origin-free (AOF) and carrier protein-free
Manufactured in our Cambridge, UK laboratories
Lyophilized from acetonitrile, TFA
- Resuspend in sterile-filtered water at >50 µg/ml, add carrier protein if desired, prepare single use aliquots and store frozen at -20 °C (short-term) or -80 °C (long-term).
Featured applications:
Differentiation of midbrain dopaminergic neurons
Differentiation of iPSC derived neural progenitors to neurons
Neural organoid growth and differentiation
- Recombinant human GDNF protein (Qk051)
- Recombinant human TGF-β1 PLUS™ protein (Qk010)
- Recombinant human CNTF protein (Qk063)
- Recombinant human DKK-1 protein (Qk068)
- Recombinant human FGF-8a protein (Qk059)
- Recombinant human FGF-8b protein (Qk057)
- Recombinant human NT-3 protein (Qk058)
- Recombinant human Shh protein (Qk055)
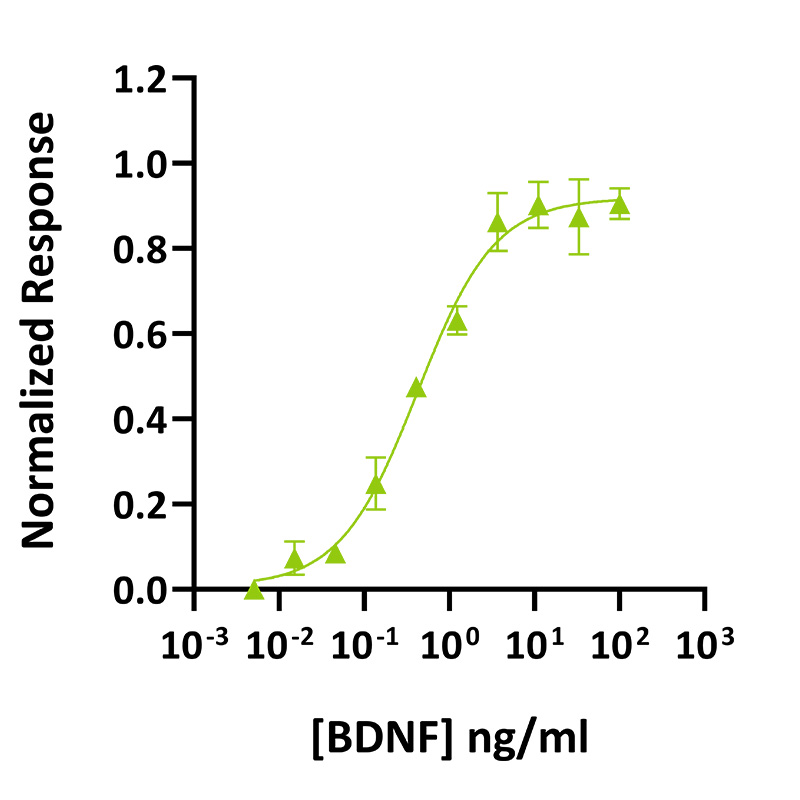
Recombinant BDNF activity was determined using a NFAT-luciferase reporter assay in transfected HEK293T cells also expressing TrkB. EC50 = 0.58 ng/ml (41 pM). Cells are treated in triplicate with a serial dilution of BDNF for 6 hours. Firefly luciferase activity is measured and normalized to the control Renilla luciferase activity. Data from Qk050 lot #104465.
Qk050 migrates as a single band at 14 kDa in non-reducing (NR) conditions and upon reduction (R). No contaminating protein bands are visible. Purified recombinant protein (3 µg) was resolved using 15% w/v SDS-PAGE in reduced (+β-mercaptothanol, R) and non-reduced (NR) conditions and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250. Data from Qk050 batch #104346.

Further quality assays
Mass spectrometry: single species with expected mass
Recovery from stock vial: >95%
Endotoxin: <0.005 EU/μg protein (below level of detection)
We are a company founded and run by scientists to provide a service and support innovation in stem cell biology and regenerative medicine. All our products are exceptionally high purity, with complete characterisation and bioactivity analysis on every lot.

Qkine BDNF was more bioactive than BDNF from an alternative supplier. Recombinant BDNF activity was determined using a NFAT-luciferase reporter assay in transfected HEK293T cells also expressing TrkB. Cells are treated in triplicate with a serial dilution of Qkine BDNF (Qk050, green) or alternative supplier BDNF (Supplier B, black) for 6 hours. Firefly luciferase activity is measured and normalized to the control Renilla luciferase activity. Data from Qk050 lot #104465.
Technote | BDNF (Qk050) bioactivityProtein background
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a member of neurotrophin family which includes nerve growth factor (NGF) and neurotrophin–3/4/5 (NT–3/4/5) [1,2]. BDNF plays a crucial role during embryonic development and the maintenance of the nervous system during adulthood. It mediates many aspects, including the survival, growth, maintenance, and differentiation of neural stem cells and mature neurons [3,4]. It stimulates neurogenesis and promotes the growth of dendrites and axons [5,6]. It is also involved in synaptic plasticity, forming and strengthening synapses in response to experience and learning [7]. Finally, it regulates the neuroprotection as it is involved in neural repair and recovery [8].
In cell culture, recombinant human BDNF supports the survival and growth of neurons and establishes and strengthens synapses. It is used in combination with other growth factors to maintain neurons and to differentiate human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neural progenitors into neurons [5]. It is used for the differentiation and maturation of dopaminergic neurons with glial-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), FGF-8a/FGF-8b, and Shh [9–11]. Glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons are maintained with combinations of BDNF, GDNF, NT-3, or insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) [12–14]. Cholinergic neurons are obtained using BDNF, IGF-1, and NGF [15,16]. Also, the culture of cortical organoids require BDNF and GDNF for maturation [17].
BDNF is released by various cells including neurons, glial cells (astrocytes and microglia), immune cells (T cells and macrophages), as well as skeletal muscles. It has several precursor isoforms and its mature active form is a dimer stabilised by a cysteine knot composed of 119 amino acids and a molecular weight of around 13 kDa [18]. The mature isoform binds to the receptor tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB) with high affinity to activate MAPK, PI3K and PLC-γ signalling cascades [19,20]. These pathways are related to the survival of neurons, growth of dendrites and axons, development of synapses, and learning- and memory-dependent synaptic plasticity19. In addition, this protein binds to p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR) with lower affinity to activate the NF-kB activation [21].
Impaired BDNF signaling has been linked to several diseases such as neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases, neurological disorders such as depression and anxiety disorders, as well as spinal cord injury [22,23]. Recombinant BDNF and other neurotrophins such as NGF and NT-3 are a growing area of research as potential targets [22,24]. For example, pharmacological agents or gene therapy could increase BDNF production and release which may have therapeutic potential for conditions like amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and depression. Also, targeted delivery of this protein could be beneficial to preserve nerve function, promote healthy brain ageing, and regenerate the loss of neurons.
Customer & collaborator data
Maintenance of iNeurons using Qkine animal origin-free BDNF
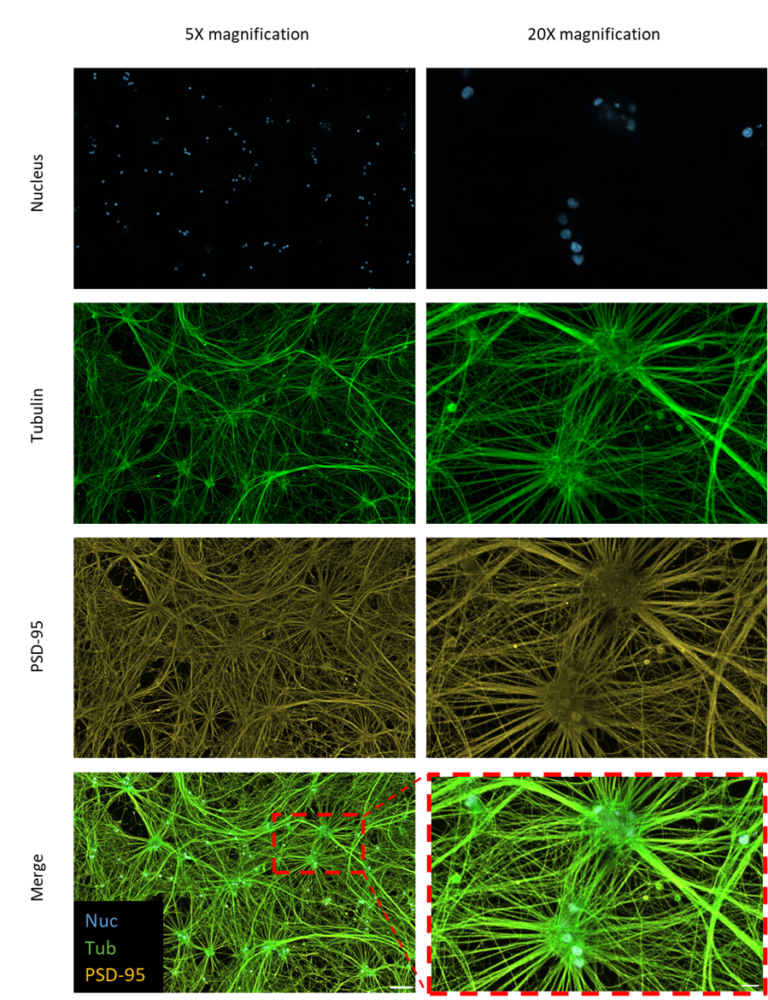
iNeurons cultured with Qkine animal-free BDNF (Qk050) developed long neurites and formed synaptic connections. They maintained a neuronal phenotype with the expression of neuron-specific, presynaptic, and postsynaptic markers.
Immunofluorescence images of iNeurons stained for postsynaptic neural markers. iNeurons were stained for the nucleus (blue), tubulin (green), and PSD-95 (yellow). Scale bars = 100 µm (5x magnification) and 20 µm (20x magnification).
In collaboration with Tong Li, Omer Bayraktar, and Maryna Panamarova, Wellcome Sanger Institute

Differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) into dopaminergic neurons
Qkine animal origin-free growth factors BDNF (Qk050), FGF8a (Qk059), GDNF (Qk051) and TGFb3 (Qk054) can supported the differentiation of iPSCs into mature dopaminergic neurons within 35 days.
Day 35 differentiated mature dopaminergic neurons (A, scale bar = 750 µM, B, scale bar = 300 µM).
Additional resources
- Technote | BDNF (Qk050) bioactivity
- Differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) into dopaminergic neurons (PDF)
- Animal origin-free BDNF and GDNF neural growth factors for enhanced iPSC-derived neuronal cultures (PDF)
- Maintenance of iNeurons using Qkine animal origin-free BDNF (PDF)
- Poster: Neural and glial cell maintenance and differentiation
- Poster: Pluripotent stem-cell derived organoids
- Brochure: Growth factors for neural and glial cell differentiation
- Brochure: Growth factors for enhanced organoid culture protocols
Publications using Recombinant human BDNF protein (Qk050)
-
Human retinal ganglion cell neurons generated by synchronous BMP inhibition and transcription factor mediated reprogramming.
Agarwal D et al.
DOI: doi: 10.1038/s41536-023-00327-x -
Differentiation of RGC Induced Neurons (RGC-iNs).
Agarwal D & Wahlin K
DOI: dx.doi.org/10.17504/protocols.io.14egn2pqzg5d/v2 -
A short sequence targets transmembrane proteins to primary cilia
Macarelli V, Harding EC, Gershlick DC, Merkle FT.
DOI: doi: 10.3390/cells13131156 -
Heterogeneity in oligodendrocyte precursor cell proliferation is dynamic and driven by passive bioelectrical properties
Pivoňková H, Sitnikov S, Kamen Y et al.
DOI: doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114873 -
Parkinson’s associated protein DJ-1 regulates intercellular communication via extracellular vesicles in oxidative stress
Page T, Musi CA, Bakker SE et al.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-5669239/v1 -
Profiling human hypothalamic neurons reveals a candidate combination drug therapy for weight loss
Chen HJC, Yang A, Mazzaferro S et al.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.07.18.549357 -
Synchronous 3D patterning of diverse CNS progenitors generates motor neurons of broad axial identity
Buchner F, Dokuzluoglu Z, Thomas J et al.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.12.13.628384 -
Neuronal differentiation and activity drive nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of the intellectual disability kinase TLK2
Nuhu-Soso L, Denton H, Goffin DL, Hahn I and Evans GJO.
DOI: doi: 10.1101/2025.02.20.639293 -
Familial ALS/FTD-associated RNA-Binding deficient TDP-43 mutants cause neuronal and synaptic dysregulation in vitro
Magarotto M, Gawne RT, Vilkaite G, Mason AS, Chen H-J
DOI: doi.org/10.1101/2025.03.26.645507 -
Proximity proteomics of primary cilia in human hypothalamic neurons
Macarelli V, Sroka TJ, Hansen JN, Axelsson U, Mick DU and Merkle FT
DOI: doi.org/10.1101/2025.05.11.653368
FAQ
Recombinant Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor is a synthetic form of BDNF. Qkine recombinant human BDNF is expressed in E. coli.
BDNF plays a crucial role during embryonic development and the maintenance of the nervous system during adulthood including the survival, growth, maintenance, and differentiation of neurons, growth of dendrites and axons, and synaptic plasticity.
NGF, GDNF, and BDNF are all part of the neurotrophins or neurotrophic factors family. They all regulate the development, growth, and survival of neurons and have more specific roles. NGF is associated with the growth and maintenance of sensory and sympathetic neurons. BDNF and GDNF are both associated with dopaminergic, glutamatergic, and GABAergic neurons. In addition, BDNF plays a crucial role in synapses formation whereas GDNF is involved in the growth and maintenance of other glial cells such as astrocytes.
The BDNF protein is encoded by the BDNF gene on chromosome 11.
Neurotrophic factors (also known as neurotrophins) include Nerve Growth Factor (NGF), Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF), Glial-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (GDNF), Neurotrophin-3 (NT-3), and Neurotrophin-4/5 (NT-4/5).
Neurotrophin proteins regulate neuronal growth and survival, neuroprotection, neurotransmitter release, synaptic function, and plasticity within the adult central and peripheral nervous system.
Neurotrophins promote the survival and growth of neurons by inhibiting apoptosis (programmed cell death) in a process called neuroprotection.
Our products are for research use only and not for diagnostic or therapeutic use. Products are not for resale.
For use in manufacturing of cellular or gene therapy products. Not intended for in vivo applications.

Receive an Amazon gift voucher when you leave us a review.
£25, $30 or €30 for reviews with an image and £10, $15 or €15 for reviews without an image