IL superfamily
IL superfamily is a large group of cytokines, including proteins known as interleukins and interleukin receptors. Members of this superfamily play pivotal roles in diverse biological processes such as immunity, inflammation, and hematopoiesis. Subgroups within the interleukin superfamily include the IL-1, IL-6, IL-10, IL-12, and IL-17 subfamilies, along with additional interleukins and receptors.
IL-1 subgroup includes IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-1RA, IL-18, IL-33, IL-36α, IL-36β, IL-36γ, IL-36RA, IL-37 and IL-38.
IL-6 subgroup includes IL-6, IL-11, CNTF, LIF, CT-1 and oncostatin (OSM).
IL-10 subgroup includes IL-10, IL-19, IL-20, IL-22, IL-24 and IL-26.
IL-12 subgroup includes IL-12, IL-23, IL-27, IL-35 and IL-39.
Beta common family IL-3, IL-5 and GM-CSF
human LIF
From the lab of Elena Carbognin and Graziano Martello, University of Padua
From the labs of Jamie A. Hackett, European Molecular Biology Laboratory EMBL-Rome, Davide Cacchiarelli, Telethon Institute of Genetics and Medicine and Graziano Martello, University of Padua.
From the lab of Graziano Martello and Francesco Argenton, University of Padova
Used:
human LIF (Qk036)
From the lab of Graziano Martello, University of Padova
From the lab of José Silva, Guangzhou Laboratory

A huge challenge in understanding human early embryo cell fate is due to limited access and ethical concerns. Recent research, however, from José C. R. Silva’s lab at Guangzhou National Laboratory, drawing from single-cell sequencing, suggests a conserved lineage specification process between human and mouse embryos. Blastoids, emerging models for early embryo development, generated solely from hnPSCs, offer insights into blastocyst formation without altering culture conditions. Self-renewing human naïve pluripotent stem cells (hnPSCs) spontaneously form blastoids in 3D culture, mimicking early human blastocysts. This process, mediated by the GSK3 inhibitor IM-12 in 5iLAF medium, involves upregulation of oxidative phosphorylation genes. hnPSCs dedifferentiate into E5 embryo-like intermediates, expressing SOX2/OCT4 and GATA6, which specify trophoblast fate by day 3, coinciding with blastoid formation. This was a fantastic paper to read as it is clear how this spontaneous blastoid formation highlights the importance of culture conditions and provides a new platform to study human embryo development in vitro, potentially reshaping our understanding of hnPSCs and embryo development.
From the lab of Nicolas Rivron, IMBA, Austrian Academy of Sciences
Used:
human LIF (Qk036)
From the labs of Austin Smith, University of Cambridge and Kevin J. Chalut, University of Exeter
Used:
human LIF (Qk036)
From the lab of Jan Żylicz, University of Copenhagen, Denmark
mouse LIF
From the lab of Luis M. Escudero, University of Sevilla
Used:
mouse LIF (Qk018)
bioRxiv preprint 2024
From the lab of David Turner, University of Liverpool, UK
Used:
mouse LIF (Qk018)
From the lab of Harry Leitch, Imperial College London
Used:
mouse LIF (Qk018)
From the labs of David A. Turner, University of Liverpool and Ben Steventon, University of Cambridge
Used:
mouse LIF (Qk018)
bioRxiv preprint (2024)
From the lab of Miha Modic, National Institute of Chemistry, Ljubljana, Slovenia
Used:
mouse LIF (Qk018)
From the lab of Elly M. Tanaka, Francis Crick Institute and the Research Institute of Molecular Pathology (IMP) of Vienna
Used:
mouse LIF (Qk018)
From the labs of James Briscoe and Elly M. Tanaka, Francis Crick Institute and the Research Institute of Molecular Pathology (IMP) of Vienna
Used:
mouse LIF (Qk018)
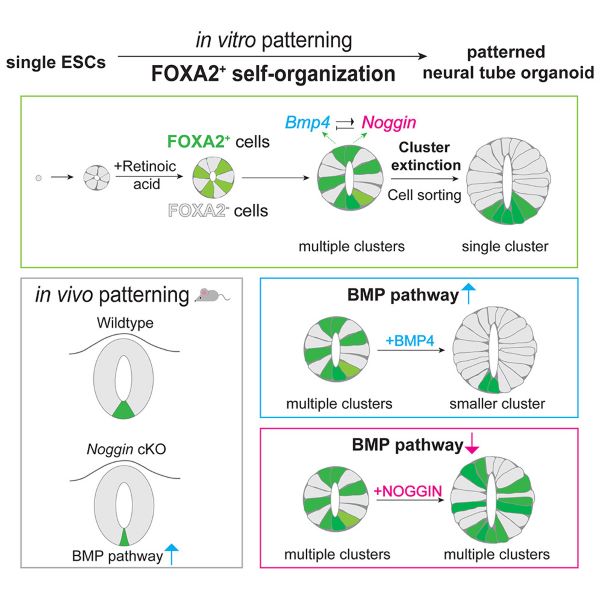
This paper gives us insight into the complex regulatory interactions between BMP-4 and noggin during neural tube development. Neural tube organoids from embryonic stem cells will organize into floorplates, without the usual inducers present in the developing embryo. They used mouse neural tube organoids and by identifying the floorplate marker FOXA2 they showed the importance of regulation of BMP-4 signaling through noggin. Noggin mutation reduced neural tube organization and floorplate formation in vitro and in vivo.
From the lab of José Silva, Guangzhou Laboratory
Used:
mouse LIF (Qk018)
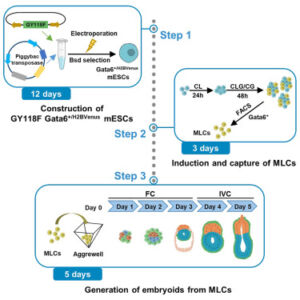
Generating cell types with properties of embryo cells with full developmental potential is of great biological importance. This paper describe steps for induction and isolation of MLCs by sorting. They explained the procedures for segregating MLCs into blastocyst cell fates and how to create embryo-like structures from them. This system provides a valuable stem-cell-based embryo model to study early embryo development.
From the lab of José Silva, Guangzhou Laboratory
Used:
mouse LIF (Qk018)
From the lab of Dr Marta Shahbazi, MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Cambridge
Reviewers comments available to view: Stadtfeld, M. Evaluation of Stuart et al.: Distinct Molecular Trajectories Converge to Induce Naive Pluripotency.
Cell Stem Cell 25, 297–298 (2019). doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2019.08.009
From the lab of José Silva, University of Cambridge
