R-spondin family
R-spondin family (RSPO) includes 4 secreted glycoproteins (R-spondin 1, R-spondin 2, R-spondin 3, R-spondin 4). Implicated in the activation and regulation of the Wnt signaling pathway, RSPO proteins contribute significantly to various biological processes throughout embryonic development, adult tissue maintenance, and the onset of disease. This family of secreted proteins is also used widely in organoid culture.
Qkine R-spondin range includes RSPO1 protein, the prototypic member of this family used to potentiate Wnt signaling in many organoid culture systems including intestinal and tumor (cancer) organoid culture. RSPO1 is also required for hematopoietic stem cell specification and cancer cell migration and survival.
We also developed a specialized form of RSPO1, R-spondin 1 LR5, engineered to act as a high affinity ligand for the LGR5 receptor. Our R-spondin family also includes Human RSPO3 protein which can be used alongside RSPO1 in intestinal organoid culture systems.
R-spondin 1
From the labs of Emmanuel Contassot and Alexander A. Navarini, University of Basel
From the lab of Sun-Young Kong, National Cancer Center, Korea
Used:
R-spondin-1 (Qk006)
From the lab of Dannielle Engle, Salk Institute for Biological Studies
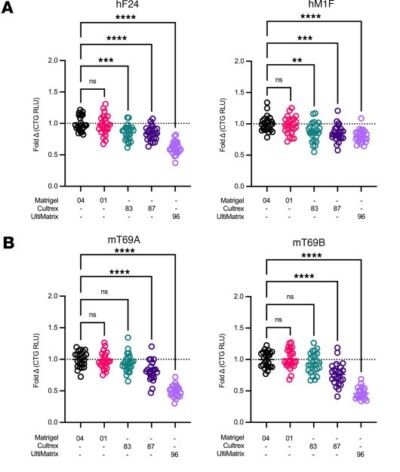
A promising application of organoids, in this case patient-derived organoids (PDOs), is to profile the therapeutic sensitivity of tumors to inform clinical decisions and to stratify patients in clinical trials more effectively. Recently there have been positive results from clinical trials giving a glimmer of the potential impact of these technologies. However, a concern is how reproducible these technologies are, particularly as most still rely on animal-derived basement membrane extracts, where batch variation is a sector-wide concern. This recent publication shows consistent drug responses are observed when different sources of commercial BME were compared. This is reassuring and speaks to how robust these approaches can be.
From the lab of Dae-Sik Lim, KAIST, Republic of Korea
Used:
R-Spondin 1 (Qk006)
