Currency
Recombinant human FGF-8b protein (Qk057)
Fibroblast growth factor 8b (FGF-8b) is a member of the FGF family involved in the regulation of embryogenesis, cellular proliferation, differentiation, and migration.
FGF-8b is commonly used for the differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cells into neural cell types and brain organoid cultures.
FGF-8b is a spliced form of FGF-8, a heparin-binding protein that targets mammary and non-mammary cells expressing the FGF receptors. A 22.5 kDa highly pure, bioactive recombinant protein produced in an animal origin-free expression system. This protein is carrier-free, tag-free and non-glycosylated to ensure a pure, homogenous protein with exceptional lot-to-lot consistency. Qk057 is suitable for enhanced reproducibility and physiologically relevant cultures.
Orders are typically shipped same or next day (except Friday).
Easy world-wide ordering, direct or through our distributors.
1000µg will be despatched as 2 x 500µg
Fast and free shipping.
Buy online with secure credit card or purchase order.
For any questions, please email orders@qkine.com
Summary
High purity human FGF-8b protein (Uniprot: P55075)
>98%, by SDS-PAGE quantitative densitometry
- 22.5 kDa
- Expressed in E. coli
Animal origin-free (AOF) and carrier protein-free
- Manufactured in our Cambridge, UK laboratories
- Lyophilized from HEPES pH 7.5, NaCl, Mannitol
Resuspend in water at >100 µg/ml, prepare single use aliquots, add carrier protein if desired and store frozen at -20°C or -80°C
Featured applications
Generation of iPSC-derived dopaminergic (DA) neurons
Generation of induced neuronal cells from reprogrammed fibroblasts
Generation of iPSC-derived midbrain organoids
Neurite outgrowth from spinal ganglion neurons
AIGF, AIGFKAL6, Androgen-induced growth factor, FGF8, FGF-8, Fibroblast Growth Factor – 8, HBGF-8, Heparin Binding Growth Factor – 8, MGC149376
human, mouse
Bioactivity
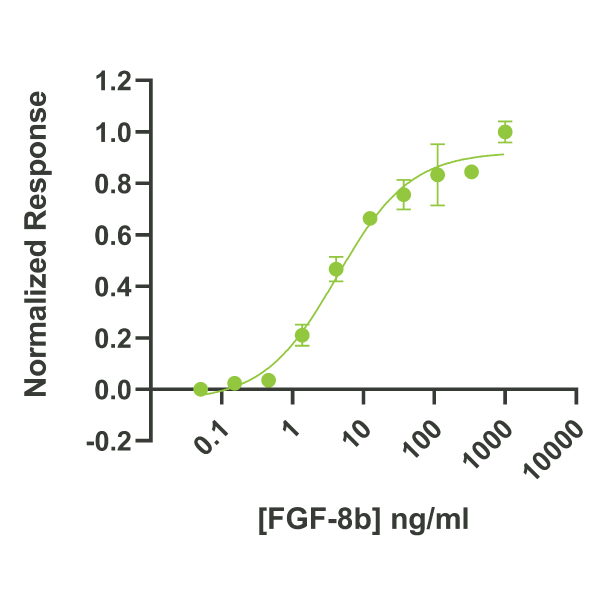
FGF-8b activity is determined using the Promega serum response element luciferase reporter assay (*) in HEK293T cells. EC50 = 4.1 ng/ml (0.18 nM). Cells are treated in triplicate with a serial dilution of FGF-8b for 3 hours. Firefly luciferase activity is measured and normalized to the control Renilla luciferase activity. Data from Qk057 lot #104458. *Promega pGL4.33[luc2P/SRE/Hygro] #E1340
Purity
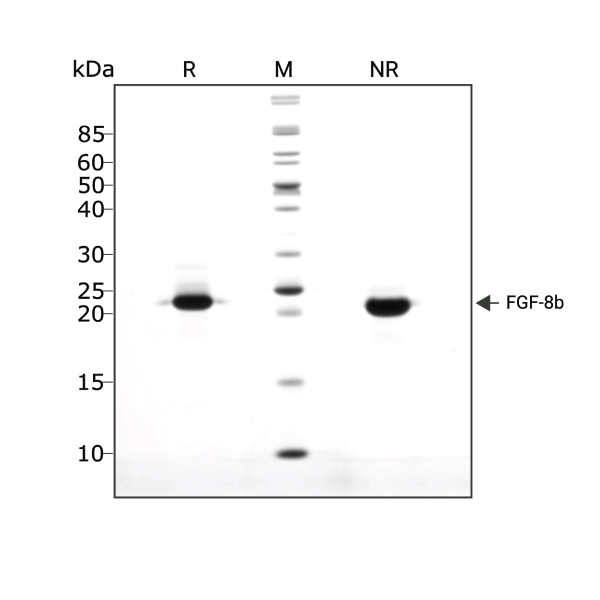
FGF-8b (Qk057) migrates as a single band at 22.5 kDa in non-reducing (NR) conditions and upon reduction. Purified recombinant protein (3 µg) was resolved using 15% w/v SDS-PAGE in reduced (+β-mercaptothanol, R) and non-reduced (NR) conditions and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250. Data from Qk057 batch #104458.
Further quality assays
- Mass spectrometry, single species with expected mass
Endotoxin: <0.005 EU/μg protein (below level of detection)
- Recovery from stock vial: >95%
We are a company founded and run by scientists to provide a service and support innovation in stem cell biology and regenerative medicine. All our products are exceptionally high purity, with complete characterisation and bioactivity analysis on every lot.
Qkine animal origin-free FGF-8b produces consistently high bioactivity lot-to-lot
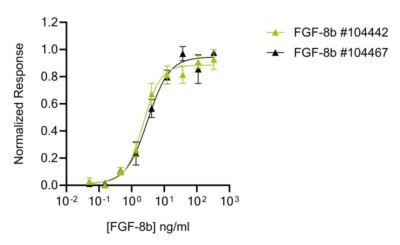
Qkine FGF-8b (Qk057) protein has exceptional lot-to-lot consistency. Bioactivity was determined using a firefly luciferase reporter assay in stably transfected HEK293T cells. Cells were treated with a serial dilution of independent lots of FGF-8b for 3 hours in triplicate.
Qkine FGF-8b is as biologically active as the comparable alternative supplier protein

Bioactivity was determined using the Promega serum response element luciferase reporter assay in transfected HEK293T cells. Cells were treated in triplicate with a serial dilution of Qkine FGF-8b (Qk057, green) or an alternative supplier protein (Supplier B, black) for 3 hours. Firefly luciferase activity was measured and normalized to the control Renilla luciferase activity.
Protein background
FGF-8b is a heparin-binding protein and an isoform of FGF-8 belonging to a family of fibroblast growth factors (FGF) [1]. It was originally discovered as an essential growth factor for the androgen-dependent growth of mouse mammary carcinoma cells [2]. In mouse, there are eight sliced protein isoforms of FGF8 (a-h) whereas in humans, there are four alternate spliced protein isoforms namely FGF-8a, FGF-8b, FGF-8e and FGF-8f. These four FGF8 isoforms (a, b, e and f) are highly conserved between humans and mice. Human and murine FGF-8a and FGF-8b show 100% homology [3] whereas there is a 98% identity with human and murine FGF8e and FGF8f [4].
Human FGF-8b, a monomeric protein has a molecular weight of 22.5kDa with 194 amino acid (aa) residues covering the signal sequence domain, N-terminal domain, FGF domain and proline-rich C terminal sequence. Its three-dimensional structure is composed of 12 beta strands arranged in two beta-sheet and short alpha-helices. The protein contains a conserved heparin-binding domain that is essential for its biological activity.
FGF-8, including the spliced forms, work by binding the FGF receptors (FGFR) to activate the Ras/MAPK signalling pathway, a key pathway that contributes to several cellular processes. In general, the FGF family is involved in broad cellular and biological processes including cell proliferation, differentiation, survival and apoptosis [5-8].
Functionally, FGF-8b has been shown to play a major role during prenatal development. It is widely expressed during embryogenesis and is a key player in epithelial-mesenchymal transitions [9]. During gastrulation, it contributes to the organization and induction role and regulates the patterning of organs in the embryos. These organs include the brain, eye, ear, limb and the heart [10-12].
Although, FGF-8 isoforms work in a coordinated and concerted manner, findings have suggested that they also have distinct key roles. FGF-8b has been shown to have the strongest affinity for the receptor and oncogenic capacity. A study using transgenic mice showed FGF-8a expands the midbrain while FGF-8b showed a transformational activity by transforming the midbrain into the cerebellum [13].
FGF-8b and other neurotrophins have been shown to promote neural regeneration. More specifically, FGF-8b has been shown to promote neurite outgrowth in mammalian spiral ganglion neurons (SGN) in vitro [14]. FGF-8b, in combination with Shh, a neurotrophic factor, and transcription factors Ascl1 and Nurr1, has been used to generate induced neuronal cells (pan-neuronal and dopaminergic (DA) neurons) by reprogramming embryonic mouse fibroblasts [15]. Additionally, FGF-8b has been used to generate DA neurons from stem cells, including induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and dental pulp stem cells [16-17]. More recently, FGF-8b has been used to generate ventral midbrain organoids derived from iPSCs to provide a robust 3D in vitro platform that is suitable for comprehensive DA neuronal studies [18].
Whilst there is a limited expression of FGF-8 and its isoforms in the normal adult, increasing studies have shown the presence of FGF-8 in adult tissues and cells including the reproductive tract, peripheral leukocytes and hematopoietic cells [19-20]. Further functional studies are required to fully delineate the role of FGF-8 and its isoforms in the normal adult.
Our products are for research use only and not for diagnostic or therapeutic use. Products are not for resale.



What others are saying
There are no contributions yet.