 Recombinant bovine HGF NK1 protein (Qk060)
Recombinant bovine HGF NK1 protein (Qk060)Recombinant bovine HGF NK1 protein (Qk060)
£125.00 – £1,400.00

Recombinant bovine HGF NK1 protein is a potent, high-purity NK1 isoform of bovine hepatocyte growth factor (HGF). Bovine HGF differs from human HGF at several key amino acid residues that are predicted to affect bioactivity and receptor binding. Use of species-specific HGF growth factor will facilitate media optimization for cellular agriculture (cultivated meat) and veterinary applications. Also available is Qk061 porcine HGF NK1. The highly scalable animal-free manufacture and enhanced bioactivity make this suitable for chemically-defined media and reproducible scale-up.
Qkine bovine HGF NK1 is a 20 kDa naturally occurring isoform of HGF, animal origin-free and carrier-protein free.
In stock
Orders are typically shipped same or next day (except Friday).
Easy world-wide ordering, direct or through our distributors.
£125.00 – £1,400.00
Fast and free shipping.
Buy online with secure credit card or purchase order. For any questions, please email orders@qkine.com
Summary:
- High purity recombinant bovine HGF protein (Uniprot: F1MZD6)
- 20 kDa
>98%, by SDS-PAGE quantitative densitometry
Expressed in E. coli
Animal origin-free (AOF) and carrier protein-free
Manufactured in our Cambridge, UK laboratories
Lyophilized from acetonitrile, TFA
- Resuspend in 10 mM HCl (Reconstitution solution A) at >50 µg/ml, add carrier protein if desired, prepare single-use aliquots and store frozen at -20 °C (short-term) or -80 °C (long-term)
Featured applications:
Cellular agriculture process development
Differentiation of iPSCs to hepatocyte-like cells
Cellular agriculture and cultivated meat cell culture media optimization
iPSC and primary cell differentiation to muscle
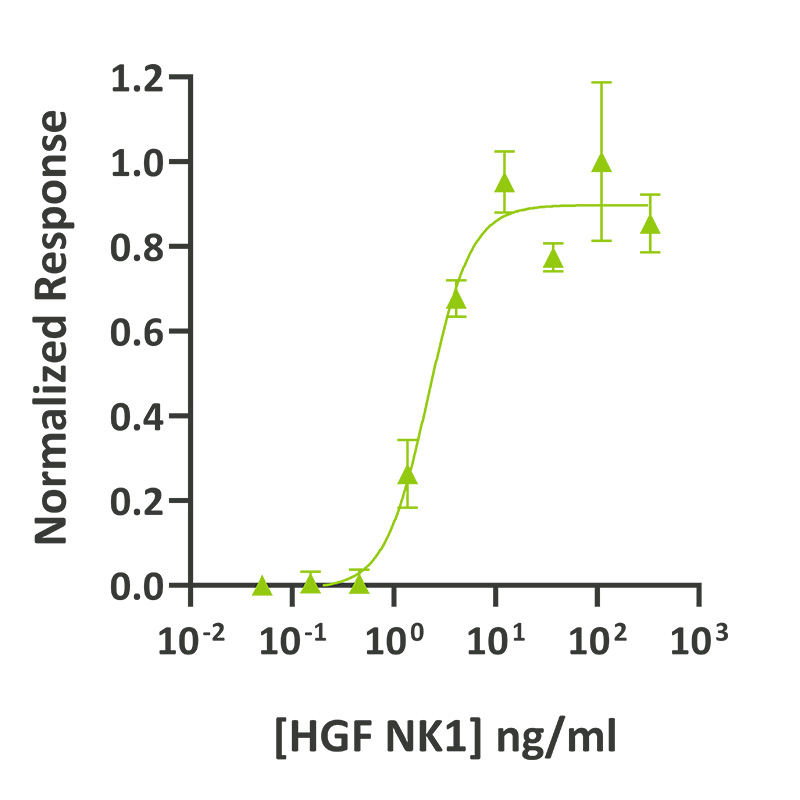
HGF NK1 activity was determined using the Promega serum response element luciferase reporter assay (*) in HEK293T cells. EC50 = 2.0 ng/ml (96 pM). Cells were treated in triplicate with a serial dilution of HGF NK1 for 3 hours. Firefly luciferase activity was measured and normalized to the control Renilla luciferase activity. Data from Qk060 lot #104408. Please note: protein activity has been determined in a standardized assay using human cells. *Promega pGL4.33[luc2P/SRE/Hygro] #E1340
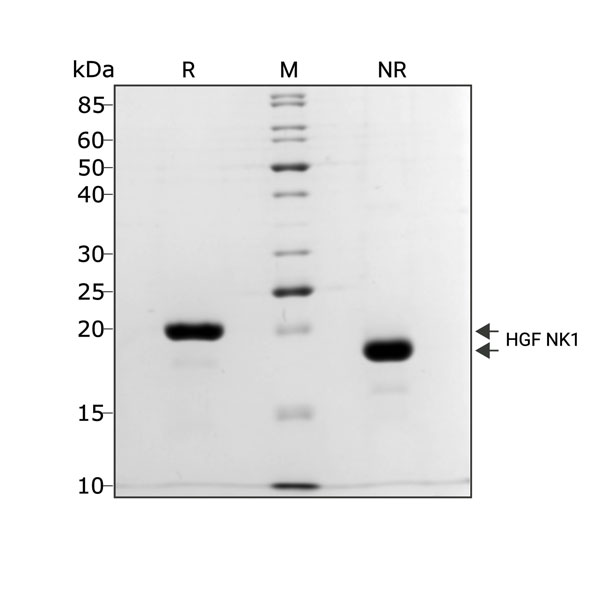
Recombinant bovine HGF protein (Qk060) migrates as a single band at 18 kDa in non-reducing (NR) conditions and 20 kDa upon reduction (R). Purified recombinant protein (3 µg) was resolved using 15% w/v SDS-PAGE in reduced (+β-mercaptothanol, R) and non-reduced (NR) conditions and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250. Data from Qk060 batch #104408.
Further quality assays
Mass spectrometry: single species with expected mass
Recovery from stock vial: >95%
Endotoxin: <0.005 EU/μg protein (below level of detection)
We are a company founded and run by scientists to provide a service and support innovation in stem cell biology and regenerative medicine. All our products are exceptionally high purity, with complete characterisation and bioactivity analysis on every lot.

Species-specificity of HGF is predicted to impact bioactivity. Bovine HGF differs from human HGF at several key amino acid residues that are predicted to affect bioactivity and receptor binding. Clustal Alignment showing sequence variation between HGF NK1 from different species. Note the lack of structural conservation at key residues, which is predicted to impact receptor binding and activation.
Protein background
Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) regulates cell growth, cell motility, and morphogenesis and plays a central role in angiogenesis, tumorogenesis, and tissue regeneration. HGF binds and activates the receptor tyrosine kinase, c-Met, activating PI3K/AKT, FAK, JNK, and ERK1/2 signaling [1].
HGF is secreted as a single inactive polypeptide and is cleaved by serine proteases into a 62-kDa heavy-chain and 32-36-kDa light-chain. A disulfide bond between the heavy and light chains produces the active, heterodimeric molecule [2]. Alternative splicing of HGF produces multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. The NK1 isoform is the smallest naturally occurring splice variant, comprising the N-terminus and first kringle domain [3].
Bovine HGF has been extensively studied for its role in muscle development. HGF is known to be involved in the proliferation of satellite cells, which are key components of skeletal muscle growth. HGF has also been observed to enhance the formation of myoblasts and induce cell fusion, leading to an increase in muscle mass and strength. Furthermore, bovine HGF increases myofibrillar protein synthesis and can help restore the normal structure of muscles damaged by injury or disease. HGF may also play a role in regulating inflammatory responses during tissue repair. In addition to its effects on skeletal muscle, HGF has also been shown to have diverse activity in other tissues such as liver, brain and kidney.
The use of HGF in cultivated meat production and cell culture media optimization is an emerging field. HGF has been shown to increase the efficiency of cell proliferation and differentiation, while also improving adhesion properties during the scale-up process. HGF has also been observed to improve cell attachment and survival in various cell types such as skeletal muscle cells and cardiomyocytes. In addition, HGF supplementation in optimized or serum-free media formulation has been effective for optimizing cell culture outcomes for several cell types in basic research studies or biopharmaceutical applications.
Human HGF and bovine HGF proteins share many similarities in terms of structure and function. However, there are certain differences between the two proteins. Bovine HGF has a much lower molecular weight than its human counterpart, as well as different biochemical properties such as higher solubility and stability. Furthermore, the bovine HGF gene contains a longer leader peptide sequence that increases its translational efficiency compared to the human HGF gene. In addition, the binding affinity of bovine HGF for tyrosine kinase receptors is significantly higher than that of human HGF, indicating that it may be more potent in mediating biological effects than human HGF.
Multiple isoforms of bovine HGF have been detected, thought to have a role in a range of biological activities and cellular responses. For example, some HGF isoforms have been observed to stimulate cell proliferation while others modulate inflammation or enhance muscle growth and repair. Less is known about the functions of HGF isoforms in bovine systems than human development. The variety of HGF isoforms present in bovine HGF increases its potential to regulate a wide range of physiological processes and may contribute to its efficacy as an ingredient for cultured meat production.
Qkine HGF NK1 is produced in an animal-free microbial system that is compatible with production at scale. We are expanding our range of innovative growth factors for cellular agriculture and cultivated meat media development to support advances in the field, please reach out to cellag@qkine.com to discuss collaboration opportunities.
FAQ
HGF stands for hepatocyte growth factor, a multifunctional cytokine.
HGF is a protein that is found in various tissues and organs throughout the body such as the liver, kidneys, lungs, pancreas, blood vessels, muscles, central nervous system, and placenta.
HGF is produced by various cell types including mesenchymal cells, hepatocytes, smooth muscle cells, epithelial cells, firbroblasts, and other stromal cells.
The alternative name of HGF is scatter factor (SF).
Yes, it is a multifunctional cytokine.
The HGF gene, also know as SF, HGFB, HPTA, F-TCF or DFNB39 provides instructions for synthesizing the protein HGF. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants, at least one of which encodes a preproprotein that is proteolytically processed to generate alpha and beta chains, which form the mature heterodimer.
HGF binds to Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (HGFR), also known as c-Met.
The Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (HGFR), also known as c-Met, is a receptor tyrosine kinase that plays a crucial role in mediating the biological effects of Hepatocyte Growth Factor (HGF). The c-Met receptor is expressed on the surface of various cell types, and its activation initiates a cascade of intracellular pathways involved in cell proliferation, migration, angiogenesis, regeneration, and embryonic development.
HGF pathway, also known as the HGF/c-Met pathway, involves a series of molecular events triggered by the binding of HGF to its receptor, c-Met. It activates downstream signalling pathways such as the RAS-RAF-MAPK, PI3K-AKT, STAT3, and Wnt/β-catenin Pathways.
In cell culture, HGF is used for various applications such as the differentiation of specific lineages in particular mesenchymal cells and the growth, survival, and maintenance of hepatocytes and endothelial cells. HGF is also used in assays to study cell cycle, division, motility, invasion, and wound healing.
Yes, HGF regulates the differentiation of mesenchymal cells into hepatocytes, osteocytes and endothelial cells.
Our products are for research use only and not for diagnostic or therapeutic use. Products are not for resale.

Receive an Amazon gift voucher when you leave us a review.
£25, $30 or €30 for reviews with an image and £10, $15 or €15 for reviews without an image