Recombinant human follistatin-resistant activin A (FRACTA) protein (Qk035)
Recombinant human follistatin-resistant activin A (FRACTA) protein (Qk035)Recombinant human follistatin-resistant activin A (FRACTA) protein (Qk035)
Price range: £230.00 through £2,900.00
Follistatin-resistant activin A (FRACTA) protein has been engineered to prevent binding to the natural inhibitor, follistatin. In vivo activin A activity is regulated by follistatin, a high-affinity inhibitor; follistatin accumulates in stem cell culture, where it inhibits activin A.
Qk035 follistatin-resistant activin A (FRACTA) has equivalent bioactivity to wild-type activin A (Qk001) but does not bind follistatin so is resistant to feedback inhibition. High purity 26 kDa dimer comprising engineered mature domain of activin A protein, animal origin-free (AOF) and carrier-protein free (CF). This specialized activin A has been developed in Marko Hyvönen’s group in the University of Cambridge.
In stock
Orders are typically shipped same or next day (except Friday).
Easy world-wide ordering, direct or through our distributors.
Price range: £230.00 through £2,900.00
Buy online with secure credit card or purchase order. For any questions, please email orders@qkine.com
Summary:
- High purity engineered follistatin-resistant activin A (FRACTA) protein
- 26 kDa (dimer)
>98%, by SDS-PAGE quantitative densitometry
Expressed in E. coli
Animal origin-free (AOF) and carrier protein-free
Manufactured in our Cambridge, UK laboratories
Lyophilized from acetonitrile, TFA
- Resuspend in 10 mM HCl (Reconstitution solution A) at >50 µg/ml, add carrier protein if desired, prepare single-use aliquots and store frozen at -20 °C (short-term) or -80 °C (long-term)
Featured applications:
Induced pluripotent and embryonic stem cell differentiation and maintenance
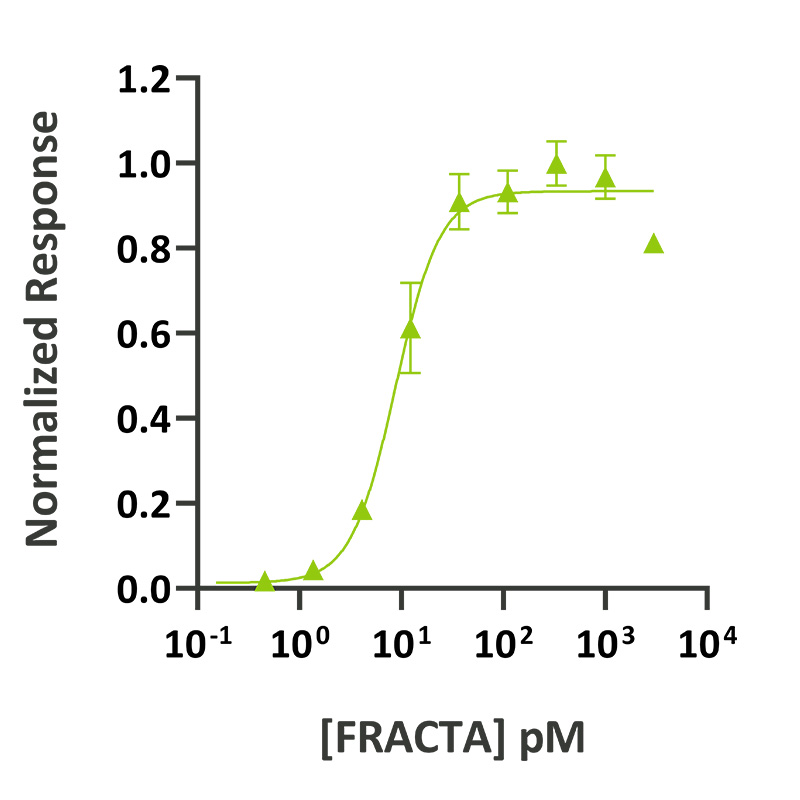
Follistatin-resistant activin A (FRACTA) activity was determined using the activin-responsive firefly luciferase reporter assay in transiently transfected HEK293T cells. Cells were treated in triplicate with a serial dilution of FRACTA. Firefly luciferase activity was measured and normalized. EC50 = 0.23 ng/ml (8.8 pM).
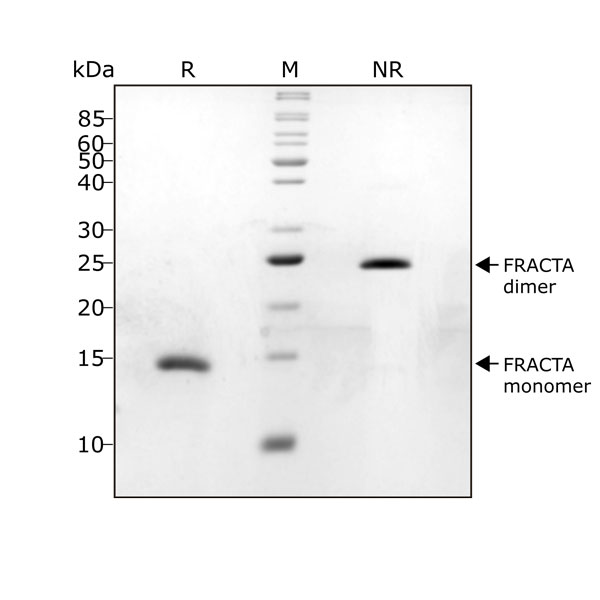
FRACTA migrates as a single band at 24 kDa in non-reducing (NR) and 13 kDa as a single monomeric species upon reduction (R). No contaminating protein bands are visible. Purified recombinant protein (1 µg) was resolved using 15% w/v SDS-PAGE in reduced (+β-mercaptothanol, R) and non-reduced conditions (NR) and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250. Data from Qk035 lot #104287.
Further quality assays
Mass spectrometry: single species with expected mass
Recovery from stock vial: >95%
Endotoxin: <0.005 EU/μg protein (below level of detection)
We are a company founded and run by scientists to provide a service and support innovation in stem cell biology and regenerative medicine. All our products are exceptionally high purity, with complete characterisation and bioactivity analysis on every lot.
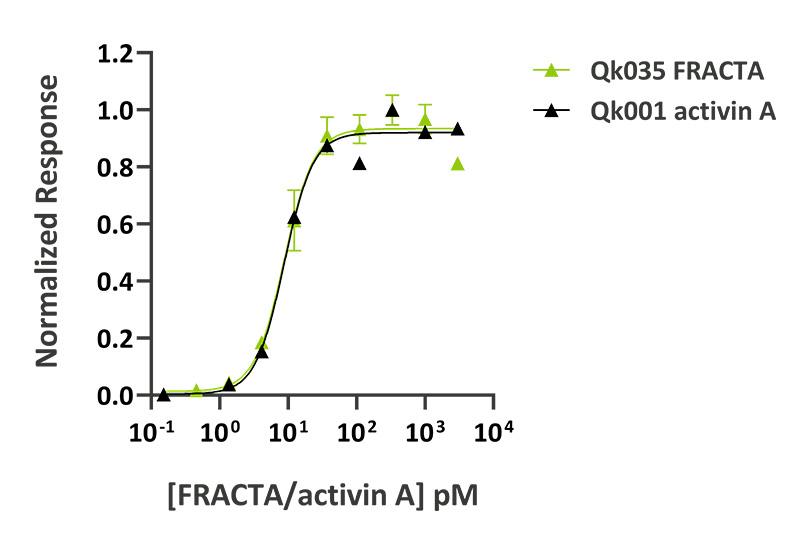
Activin A protein activity was determined using an activin-responsive firefly luciferase reporter in HEK293T cells. EC50 for wild-type activin A (Qk001) = 0.23 ng/ml (8.8 pM), EC50 for follistatin-resistant activin A (FRACTA, Qk035) = 0.22 ng/ml (8.8 pM).
Technote | Follistatin-resistant activin A (FRACTA) (Qk035) vs activin A (Qk001)Protein background
Human activin A protein is a member of the TGF-β superfamily of growth factors involved in stem cell differentiation and maintenance, regulation of embryogenesis, development of the reproductive system, wound healing and regulation of immune responses. Activin A signaling is modulated by the glycoprotein follistatin, production is which is stimulated by activin A forming a feedback loop [1], and inhibins.
Follistatin binds to and neutralises members of the TGF-β superfamily, preventing signalling by shielding the type II and I receptor binding sites [2-4].
Activins are disulfide-linked homo- and heterodimers of four inhibin β chains. The best characterized are activin A and activin B, homodimers of inhibin βA and inhibin βB respectively. Activins, like all other members in the TGF-β superfamily, are synthesized as larger precursors consisting of an N-terminal signal peptide, a pro-domain of 250–350 residues and a highly conserved mature domain. The pro-domain, which is cleaved off in the mature protein, has important roles in the biosynthesis, stabilization, transportation and signalling of the growth factors [5].
Recombinant activin A is used for maintenance of pluripotency in many human induced-pluripotent stem cell and human embryonic stem cell lines [3], and to induce stem cell differentiation into endoderm [6] and other cell fates.
Follistatin resistant activin A (FRACTA) has been developed in the lab of Marko Hyvönen at the University of Cambridge. FRACTA has been engineered to be unimpeded by follistatin while maintaining its ability to bind type I and II receptors. Read more about FRACTA.
FAQ
Activin A is a multifunctional protein. It is involved in regulating embryonic development, cell proliferation, and differentiation. It promotes the patterning and differentiation of various organs, including the development of the mesoderm, neural, and reproductive systems. It is also involved in maintaining homeostasis, regulating immune responses, and wound healing. Finally, it stimulates the release of follicle-stimulating hormone from the pituitary gland.
Activin A is a critical factor in stem cell culture, commonly used to maintain the pluripotency of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and embryonic stem cells (ESCs). It is integral to various stem cell differentiation protocols, guiding the differentiation of the definitive endoderm, neural and mesodermal lineages. Activin A is also commonly utilized in the development and maintenance of organoids.
Activin A and inhibin A are closely related proteins in the TGF-β superfamily. They share structural similarities but have distinct functions and roles in regulating various physiological processes. Activin A has broader functions beyond reproduction, which include handling embryonic development, stem cell maintenance, and the immune system. Inhibin A, conversely, is more specifically associated with the feedback control of follicle-stimulating hormones in the context of reproductive physiology.
Activin A binds to activin type I (ALK4 or ALK7) and type II (ActRIIA or ActRIIB) receptors to activate downstream SMAD signalling.
Yes, activin is involved in a feedback loop that regulates the secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinising hormone (LH).
The activin gene family includes several genes that encode different activin subunits, forming various activin isoforms such as Inhibin Beta Subunits (INHBA / INHBB / INHBC / INHBD).
Follistatin and inhibins tightly regulate activin A activity in a feedback loop.
Our products are for research use only and not for diagnostic or therapeutic use. Products are not for resale.
For use in manufacturing of cellular or gene therapy products. Not intended for in vivo applications.

Receive an Amazon gift voucher when you leave us a review.
£25, $30 or €30 for reviews with an image and £10, $15 or €15 for reviews without an image