Recombinant human IFN-gamma protein (Qk117)
Recombinant human IFN-gamma protein (Qk117)Recombinant human IFN-gamma protein (Qk117)
Price range: £160.00 through £800.00
IFN-gamma (interferon-gamma) is a cytokine crucial for immune responses, produced by T cells and natural killer cells. It activates macrophages, enhances antigen presentation, and plays a key role in inflammation.
Qkine has optimised the IFN-gamma manufacture process to produce a highly bioactive protein with excellent lot-to-lot consistency for enhanced experimental reproducibility. Qkine IFN-gamma is a highly pure 16.8 kDa protein, animal origin-free (AOF) and carrier-protein-free (CF).
In stock
Orders are typically shipped same or next day (except Friday).
Easy world-wide ordering, direct or through our distributors.
Price range: £160.00 through £800.00
Buy online with secure credit card or purchase order. For any questions, please email orders@qkine.com
Summary:
- High purity human IFN-gamma protein (UniProt number: P01579)
- 16.9 kDa (monomer)
>98%, by SDS-PAGE quantitative densitometry
Expressed in E. coli
Animal origin-free (AOF) and carrier protein-free
Manufactured in our Cambridge, UK laboratories
Lyophilized from HEPES, mannitol
- Resuspend in sterile-filtered water at >50 µg/ml, add carrier protein if desired, prepare single use aliquots and store frozen at -20 °C (short-term) or -80 °C (long-term).
Featured applications:
Antigen presentation enhancement
Autoimmune disease research
Cancer immunotherapy
Hematopoietic stem cell regulation
Immunoregulatory function
Involvement in infectious diseases
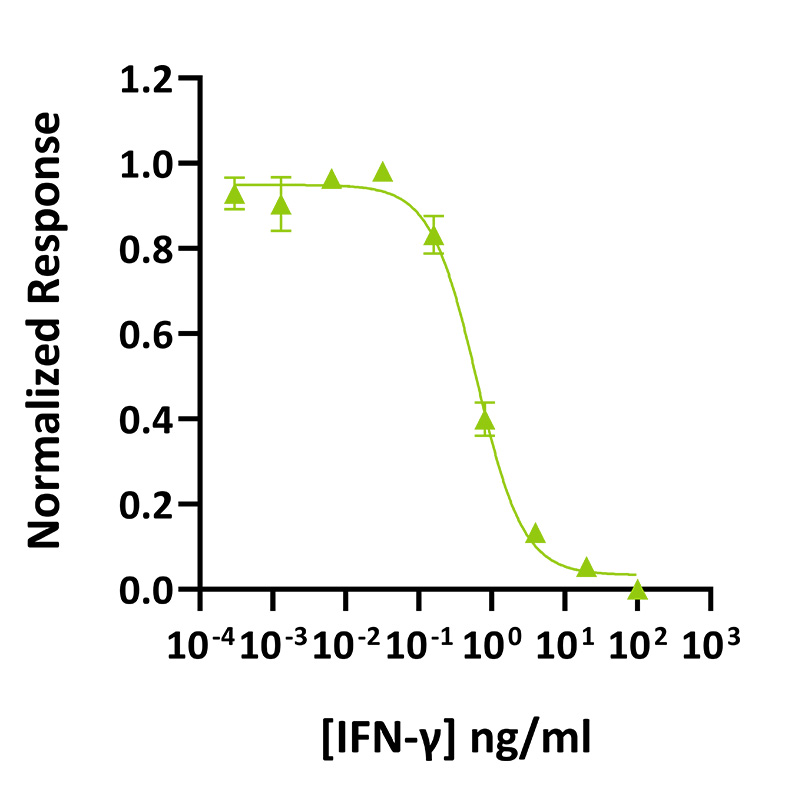
Recombinant IFN-gamma activity was determined using a cytotoxicity assay. HT-29 cells were treated in triplicate with a serial dilution of IFN-gamma for 88.5 hours. Cell viability was measured using the CellTiter 96 AQueous Cell Proliferation Assay (Promega). Assay was performed by SBH Sciences. Data from Qk117 lot 204692. EC50 = 0.62 ng/mL (37 pM).
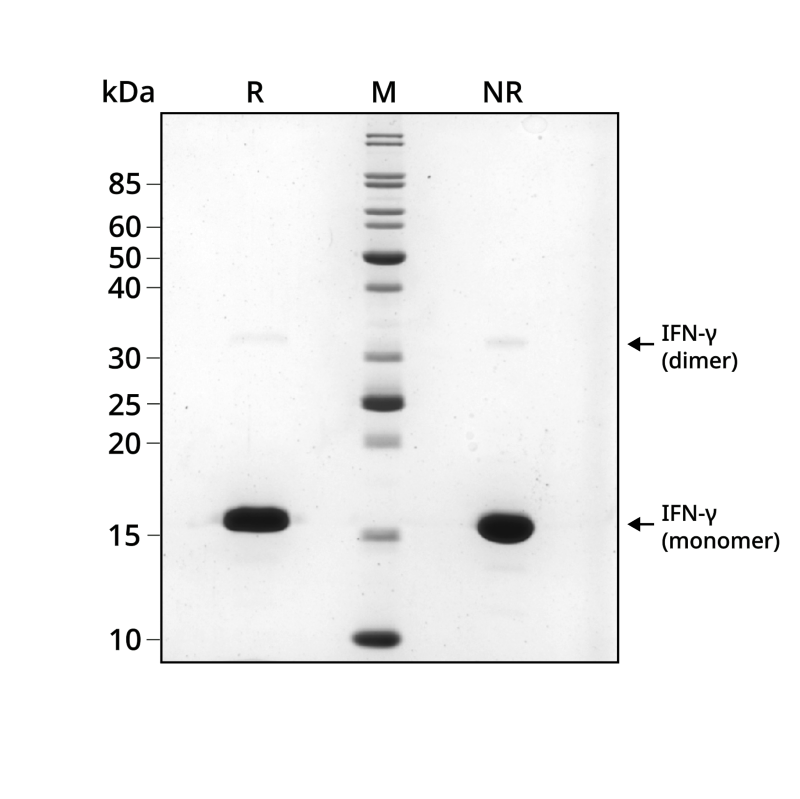
Recombinant IFN-gamma monomer migrates at approximately 17 kDa (monomer) in reduced (R) and non-reduced (NR) conditions. The dimeric form is also observed at approximately 34 kDa. No contaminating protein bands are present. The purified recombinant protein (3 µg) was resolved using 15% w/v SDS-PAGE in reduced (+β-mercaptoethanol, R) and non-reduced (NR) conditions and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250. Data from Qk117 lot #204692.

Further quality assays
Mass spectrometry: single species with expected mass
Recovery from stock vial: >95%
Endotoxin: <0.005 EU/μg protein (below level of detection)
We are a company founded and run by scientists to provide a service and support innovation in stem cell biology and regenerative medicine. All our products are exceptionally high purity, with complete characterisation and bioactivity analysis on every lot.
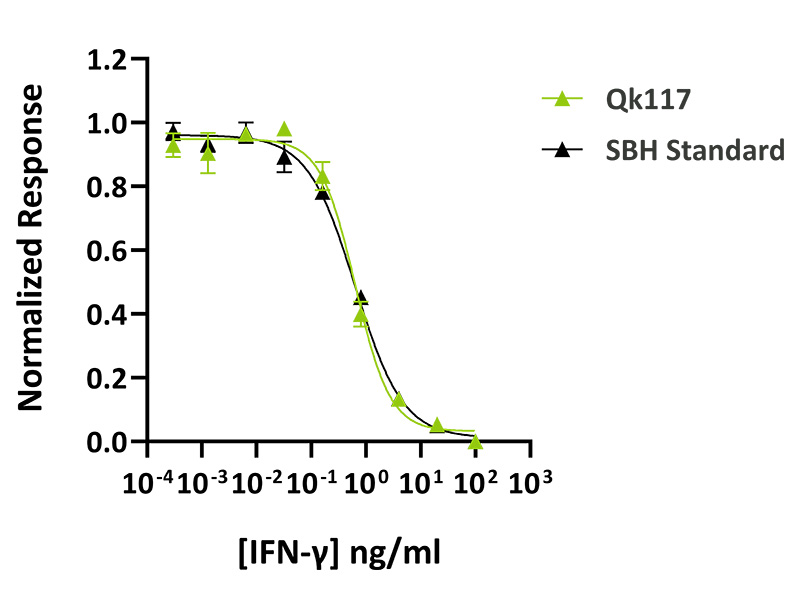
Qkine IFN-gamma is as biologically active as a comparable alternative standard protein. Recombinant IFN-gamma activity was determined by a cytotoxicity assay using HT-29 cells. Cells were treated in duplicate with a serial dilution of Qkine IFN-gamma (Qk117, green) for 88.5 hours. Cell viability was measured using the CellTiter 96 AQueous Cell Proliferation Assay (Promega). Assay was performed by SBH Sciences using their standard (black) for comparison. Data from Qk117 lot #204692.
Technote | IFN-gamma (Qk117) bioactivityProtein background
IFN-gamma (interferon-gamma / IFN-γ) is a cytokine and a critical player in the immune response. It is primarily produced by T cells (particularly CD4+ and CD8+ T cells) and natural killer (NK) cells, and it plays a pivotal role in immune modulation, particularly in activating macrophages, enhancing antigen presentation (e.g., MHC I and II), and driving the Th1 immune response. IFN-gamma also has antiviral, antiproliferative, and immunoregulatory functions [1].
IFN-gamma is a non-covalent dimer with α-helical regions contributing to its overall structure, it binds to the interferon-gamma receptor (IFNGR), a transmembrane receptor composed of two subunits: IFNGR1 and IFNGR2. Upon binding to this receptor, IFN-gamma triggers the JAK-STAT signaling pathway, leading to the transcription of interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs) involved in immune regulation [1].
IFN-gamma is widely used for its immunomodulatory effects. One key application is cancer immunotherapy, which enhances the immune system’s ability to detect and eliminate tumor cells. It is also crucial in studying autoimmune diseases, as excessive production is linked to conditions like multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis [2].
IFN-gamma is commonly used in cell culture to mimic an inflammatory environment. For example, it can be applied to macrophages or other immune cells to activate them and study their response to pathogens or cancer cells. Its role in promoting antigen presentation is also exploited in vaccine development, where it boosts the efficacy of immune responses against pathogens [3].
Additional resources
FAQ
IFN-gamma is a cytokine crucial for immune responses, produced by T cells and natural killer cells. It activates macrophages, enhances antigen presentation, and plays a key role in inflammation.
IFN-gamma is primarily produced by activated T cells (especially CD4+ Th1 cells and CD8+ cytotoxic T cells) and natural killer (NK) cells. It is found in tissues and the bloodstream, particularly at sites of infection or inflammation where immune responses are active.
Yes, IFN-gamma is a cytokine, playing a vital role in immune regulation, particularly in promoting inflammation.
The IFN-gamma gene (IFNG) encodes the IFN-gamma protein, a cytokine that regulates immune responses.
IFN-gamma binds to the IFN-gamma receptor (IFNGR), a heterodimer composed of two subunits: IFNGR1 and IFNGR2.
The IGF-2 receptor (IGF-2R), also known as the mannose-6-phosphate receptor (M6P receptor), functions in regulating IGF-2 levels by binding to and facilitating its degradation. Unlike the IGF-1 receptor, IGF-2R does not promote cell growth or survival. Instead, it acts as a scavenger receptor, helping to control IGF-2 activity and prevent excessive cell proliferation.
The IFN-gamma pathway involves IFN-gamma binding to its receptor, activating JAKs, and phosphorylating STAT1. This leads to STAT1 dimerization and translocation to the nucleus, where it regulates gene expression related to antigen presentation, inflammation, and immune cell activation.
IFN-gamma is used to activate immune cells, induce differentiation, modulate immune responses, and influence stem cell behavior. IFN-gamma helps study infection models, cancer research, and cytokine secretion by enhancing antigen presentation.
Our products are for research use only and not for diagnostic or therapeutic use. Products are not for resale.
For use in manufacturing of cellular or gene therapy products. Not intended for in vivo applications.

Receive an Amazon gift voucher when you leave us a review.
£25, $30 or €30 for reviews with an image and £10, $15 or €15 for reviews without an image