Currency
Recombinant human IL-7 protein (Qk095)
Interleukin-7 (IL-7) is a vital cytokine essential for immune system regulation, particularly in the development and maintenance of T cells, playing a crucial role in both adaptive and innate immune responses. Recombinant human IL-7 stimulates the development of lymphoid progenitor cells.
Qkine has optimized the IL-7 manufacture process to produce a highly bioactive protein with excellent lot-to-lot consistency for enhanced experimental reproducibility. IL-7 is a highly pure 17.5 kDa monomer, animal origin-free (AOF) and carrier-protein-free (CF).
Orders are typically shipped same or next day (except Friday).
Easy world-wide ordering, direct or through our distributors.
1000µg will be despatched as 2 x 500µg
Fast and free shipping.
Buy online with secure credit card or purchase order.
For any questions, please email orders@qkine.com
Summary
High purity human IL-7 protein (Uniprot number: P13232)
>98%, by SDS-PAGE quantitative densitometry
Source: Expressed in E. coli
17.5 kDa monomer
Animal origin-free (AOF) and carrier protein-free
Manufactured in Cambridge, UK
Lyophilized from Acetonitrile and Trifluoroacetic acid
Resuspend in water at >100 µg/ml, prepare single-use aliquots, add carrier protein if desired, and store frozen at -20oC or -80oC
Featured applications
Development, survival, and function of T cells
Maintenance of naive and memory T cells, crucial for immune surveillance and long-term immune memory
Development and formation of B cells
Development and formation of NK cells
Enhancement of immune responses in diseases like cancer, HIV, and during immune reconstitution following bone marrow transplantation
Development of regenerative medicine and vaccines
Interleukin 7
human
species similarity:
mouse – 56%
rat – 57%
porcine – 69%
bovine – 71%
Frequently used together
Recombinant human SCF protein (Qk078)
Recombinant human Flt3L protein (Qk087)
Recombinant human GM-CSF protein (Qk076)
Recombinant human IL-2 protein (Qk089)
Recombinant human IL-15 (coming soon)
Recombinant human IL-21 (coming soon)
Related Applications
IL-7 for hematopoietic stem cell culture
IL-7 for lymphoid differentiation
IL-7 for immune response enhancement
Bioactivity
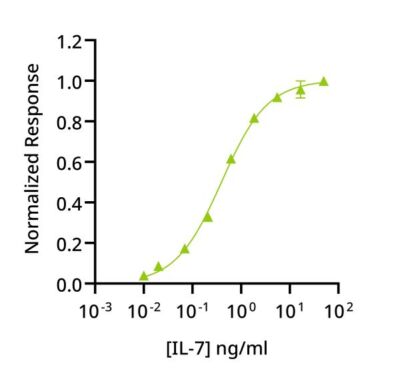
Recombinant IL-7 activity was determined using proliferation of mouse-derived B lymphocyte cell line 2E8. Cells were treated in duplicate with a serial dilution of IL-7 for 65 hours. Cell viability was measured using the CellTiter 96® Aqueous Non-Radioactive Cell Proliferation Assay (Promega). Data from Qk095 lot 204669. EC50 = 0.40 ng/ml (23 pM).
Purity
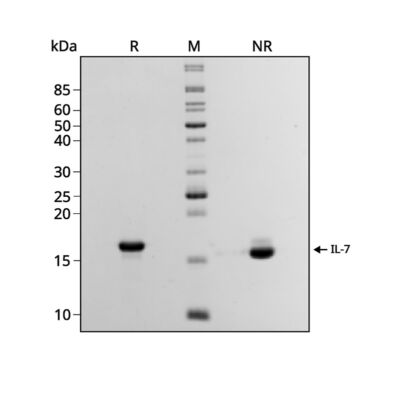
Recombinant IL-7 migrates as a major band at approximately 17.5 kDa (monomer) in reduced (R) and non-reduced (NR) conditions. No contaminating protein bands are present. The purified recombinant protein (3 µg) was resolved using 15% w/v SDS-PAGE in reduced (+β-mercaptoethanol, R) and non-reduced (NR) conditions and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250. Data from Qk095 lot #204669.
Further quality assays
Mass spectrometry, single species with the expected mass
Endotoxin: <0.005 EU/μg protein (below the level of detection)
Recovery from stock vial: >95%
We are a company founded and run by scientists to provide a service and support innovation in stem cell biology and regenerative medicine. All our products are exceptionally high purity, with complete characterisation and bioactivity analysis on every lot.
Qkine IL-7 is as biologically active as a comparable alternative supplier IL-7 protein
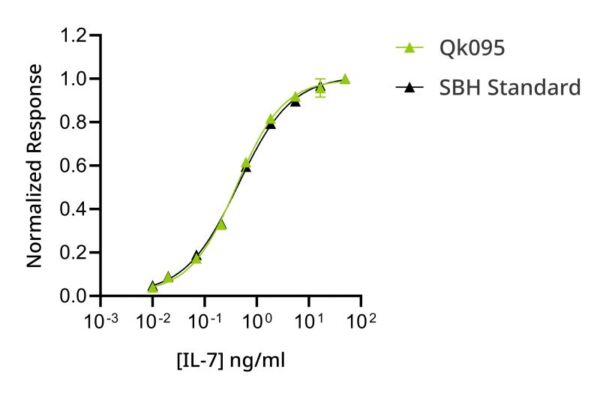
Recombinant IL-7 activity was determined using proliferation of the mouse-derived B lymphocyte cell line 2E8. Cells were treated in duplicate with a serial dilution of Qkine IL-7 (Qk095, green) for 65 hours. Cell viability was measured using the CellTiter 96 Aqueous Non-Radioactive Cell Proliferation Assay (Promega). Assay was performed by SBH Sciences using their standard (black) for comparison. Data from Qk095 lot #204669.
Protein background
IL-7 is a non-glycosylated protein with a molecular weight of about 17.5 kDa. It features four alpha-helices that facilitate its interaction with the IL-7 receptor (IL-7R), a heterodimer consisting of the IL-7Rα chain (CD127) and the common gamma chain (γc, CD132). This binding initiates signaling through the JAK-STAT pathway, particularly involving STAT5 phosphorylation, which promotes T cell survival, proliferation, and differentiation [1].
IL-7 is essential for the survival and homeostasis of T cells, supporting the development of thymocytes in the thymus and maintaining naive and memory T cells in the periphery, thus ensuring effective immune surveillance and long-term memory [2]. IL-7 influences B cell development and plays a role, though less prominently, in the development of natural killer (NK) cells [2].
IL-7 is extensively studied for its potential in cancer immunotherapy, where it enhances immune responses, particularly in promoting T cell recovery following chemotherapy or radiation, and in combination with checkpoint inhibitors [4]. In HIV and other chronic infections, IL-7 is explored for its ability to restore immune function by increasing CD4+ T cell counts and reducing immune exhaustion, potentially improving the effectiveness of existing therapies [3]. IL-7 also plays a key role in bone marrow transplantation, where it accelerates T cell recovery, reduces immune vulnerability, and is studied for its potential to mitigate graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) [4, 5].
In autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis, IL-7 is a target for controlling autoreactive T cell survival and proliferation, offering new therapeutic approaches [5]. IL-7 is investigated as a vaccine adjuvant, particularly in vaccines requiring strong T cell responses, and in regenerative medicine, where its role in expanding T cells and hematopoietic stem cells is harnessed to enhance the efficacy of immune system regeneration therapies [4-6].
Additional resources
FAQ
IL-7 is an essential cytokine involved in the development, survival, and maintenance of T-cells, crucial for the immune response. It supports T-cell homeostasis, aids in B-cell development, and is being studied for therapeutic potential in immunodeficiency disorders, cancer treatment, and enhancing vaccine responses by boosting immune function.
IL-7 is primarily produced by stromal cells in the bone marrow and thymus. It is also found in secondary lymphoid organs, such as lymph nodes, and is produced by non-lymphoid tissues like the skin, gut, and liver.
Yes, IL-7 is a cytokine. Cytokines are signaling molecules that mediate and regulate immunity, inflammation, and hematopoiesis.
The IL-7 gene encodes the protein interleukin-7 (IL-7), which is a cytokine critical for the development and maintenance of the immune system, particularly in T cells.
IL-7 binds to the IL-7 receptor, composed of the IL-7Rα (CD127) and the common gamma chain (γc, CD132).
The IL-7 receptor (IL-7R) functions to mediate the survival, proliferation, and differentiation of T cells. It does this by binding IL-7 and triggering signaling pathways, particularly the JAK-STAT pathway, which promotes T cell development in the thymus, maintains peripheral T cell homeostasis, and supports early B cell development.
The IL-7 pathway involves IL-7 binding to its receptor, activating the JAK-STAT signaling cascade, which promotes T cell survival, proliferation, and differentiation.
IL-7 is used to support the growth, survival, and proliferation of T cells and B cell precursors. It’s particularly vital in expanding T cells for research, immunotherapy, and studying immune cell development in vitro.
Our products are for research use only and not for diagnostic or therapeutic use. Products are not for resale.


What others are saying
There are no contributions yet.