Currency
Recombinant human M-CSF protein (Qk075)
Macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) is a cytokine that regulates the survival, proliferation, differentiation, and functional activation of monocytes, such as macrophages and dendritic cells.
M-CSF has been used in vitro for the differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived macrophages as well as the maintenance and development of monocytes in hematopoietic stem cell culture. M-CSF has also been used to influence macrophage polarization towards an anti-inflammatory or M2 macrophage phenotype.
Qkine M-CSF is a highly bioactive, animal origin-free (AOF), carrier protein-free 36.8 kDa recombinant protein with exceptional lot-to-lot consistency.
Orders are typically shipped same or next day (except Friday).
Easy world-wide ordering, direct or through our distributors.
1000µg will be despatched as 2 x 500µg
Fast and free shipping.
Buy online with secure credit card or purchase order.
For any questions, please email orders@qkine.com
Summary
High purity human M-CSF protein (Uniprot: P09603)
>98%, by SDS-PAGE quantitative densitometry
Expressed in E. coli
36 kDa dimer
Animal origin-free (AOF)
Carrier protein-free
Manufactured in our Cambridge, UK laboratories
Lyophilized from acetonitrile/TFA
Resuspend in 10 mM HCl, prepare single-use aliquots, add carrier protein if desired and store frozen at -20oC or -80oC
Featured applications
Differentiation of iPSC-derived macrophages
Culture of bone marrow-derived macrophages
Maintenance of macrophages
Osteoclast culture
Polarization of anti-inflammatory or M2 macrophage
Differentiation of alveolar macrophages to study fibrotic disorders
Colony-stimulating factor-1, CSF-1, CSF1, macrophage colony stimulating factor, macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1, M-CSF, MCSF, Lanimostim, Flanimostim, MGC31930
human
species similarity:
mouse – 74%
rat – 54%
bovine – 66%
Frequently used together
Bioactivity

M-CSF activity is determined using the proliferation of NFS-60 mouse myeloid leukemia cells. Cells are treated in triplicate with a serial dilution of M-CSF for 48 hours. Cell viability is measured using the CellTiter-Glo (Promega) luminescence assay and normalized. EC50 = 196 pM (7.2 ng/mL). Data from Qk075 lot #204507.
Purity
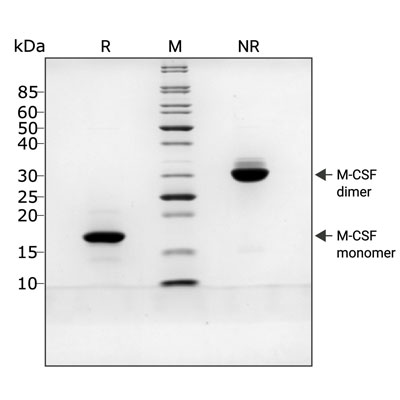
Recombinant M-CSF migrates as a major band at approximately 36 kDa (dimer) in non-reducing (NR) conditions. Upon reduction (R), only the monomer band at approximately 18 kDa is visible. No contaminating protein bands are present. The purified recombinant protein (3 µg) was resolved using 15% w/v SDS-PAGE in reduced (+β-mercaptoethanol, R) and non-reduced (NR) conditions and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250. Data from Qk075 batch #204507.
Further quality assays
- Mass spectrometry, single species with expected mass
Endotoxin: <0.005 EU/μg protein (below level of detection)
Recovery from stock vial: >95%
We are a company founded and run by scientists to provide a service and support innovation in stem cell biology and regenerative medicine. All our products are exceptionally high purity, with complete characterisation and bioactivity analysis on every lot.
Qkine M-CSF is as biologically active as a comparable alternative supplier protein
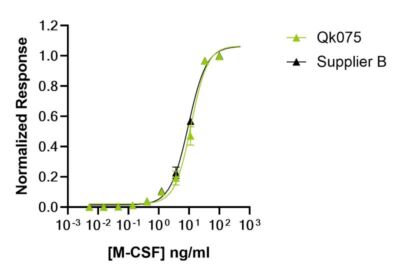
M-CSF activity was determined using the proliferation of NFS-60 mouse myeloid leukemia cells. Cells were treated in triplicate with a serial dilution of Qkine M-CSF (Qk075, green) or M-CSF from an alternative supplier (Supplier B, black) for 48 hours. Cell viability was measured using the CellTiter-Glo (Promega) luminescence assay and normalized. Data from Qk075 lot #204507.
Protein background
Macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) or colony-stimulating factor-1 (CSF-1), is a secreted glycoprotein belonging to the family of hematopoietic growth factors [1]. It is a cytokine which regulates the survival, proliferation, and renewal of monocytes and macrophages [2–4]. It plays a key role in the differentiation of progenitors to the monocyte-macrophage lineage and the functional activation of mature macrophages [4]. It is also involved in the growth and differentiation of other myeloid cells such as dendritic cells and osteoclasts [5]. M-CSF was the first CSF to be isolated and purified [2]. Other growth factors involved in the regulation of monocyte/macrophage include GM-CSF, IL-3, and IFN-γ [6,7].
Human M-CSF has a molecular weight of 36 kDa [8]. It is expressed as three functionally major isoforms: a secreted chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan, a secreted glycoprotein, and a membrane-spanning cell-surface glycoprotein [9]. All three isoforms share the same amino terminal of 149 amino acids required for biological activity [9,10]. The overall topology of M-CSF is dimeric and composed of two covalently linked four-helix bundles forming a flat and elongated structure [10].
Various cells produce and release M-CSF such as endothelial cells, fibroblasts, osteoblasts, smooth muscle, and macrophages [11–14]. M-CSF binds to CSF-1 receptor (CSF-1R), a receptor tyrosine kinase expressed at the surface of bone marrow-derived macrophages, monocytes, microglial cells, as well as osteoclasts and dendritic cells [15–17]. The M-CSF/CSF-1R binding leads to the activation through dimerization of the PI3K-AKT and AMPK signaling cascades involved in macrophage differentiation [16,18].
Low levels of M-CSF stimulate microglia survival while elevated levels of M-CSF stimulate cell proliferation and migration [16,19]. Elevated levels of M-CSF usually result from inflammatory conditions or from immunosuppressive conditions when the tumour microenvironment recruits tumor-associated macrophages [16]. Hence, the M-CSF/CSF-1R axis has gained attention for its potential as a target for neurological disorders such as glioma or stroke [16].
M-CSF has been used in vitro for the differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSCs)-derived macrophages as well as the maintenance and development of monocytes in hematopoietic stem cell culture [20,21]. In a pluripotent stem cell-based hematopoietic differentiation model, M-CSF along with IL-3 directed myeloid cells to monocyte/macrophage-type cells able to phagocytose and secrete cytokines [21]. In mouse hematopoietic stem cells, M-CSF can instruct myeloid cell-fate change by inducing the myeloid master regulator PU.1 [20]. M-CSF has also been used to influence macrophage polarization. Indeed, previous publications have reported that M-CSF induces an anti-inflammatory or M2 macrophage phenotype [22,23]. Finally, Lescoat et al. have identified human blood monocyte-derived macrophages differentiated with M-CSF as a relevant in vitro model to study alveolar macrophages in fibrotic disorders [24].
Additional resources
Our products are for research use only and not for diagnostic or therapeutic use. Products are not for resale.


What others are saying
There are no contributions yet.